Effects of Sun Rays on Children
- Effects of Sun Rays on Children
- What are Sun Rays?
- What Should We Do to Reduce the Negative Effects of the Sun on Children?
- What Should You Do First for Children Exposed to Heatstroke?
Dear parents, on this day when school holidays begin, I would like to share information about the effects of sun rays on children. While the sun is an important source of life, it also poses potential risks that can affect our health. Children, especially with their sensitive skin, are more susceptible to the sun. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the effects of the sun and protect your children accordingly.
What are Sun Rays?
Sun rays are divided into various components: visible light, infrared rays, and ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV rays have the most significant impact on children's skin. They are classified into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin tissues, while UVB rays have a more superficial effect. UVC rays are absorbed by the atmosphere and do not reach the Earth. UV rays can cause sunburns, heatstroke, and even skin cancer on children's skin.
What Should We Do to Reduce the Negative Effects of the Sun on Children?
Exposure to the sun can lead to long-term health problems for children. Infants and young children, in particular, are more sensitive to the sun. Here are some important steps to reduce the negative effects of the sun on children:
- Control Sun Exposure Hours: The intensity of sun rays is higher, especially between 10:00 AM and 4:00 PM. Try to keep your children out of the sun as much as possible during these hours.
- Utilize Shade: If the weather is hot and sunny, encourage your children to play in shaded areas when spending time outside. Shady spots under trees or umbrellas can protect your children from the harmful effects of the sun.
- Pay Attention to Clothing Choices: Make sure to dress your children appropriately when they go out in the sun. Choose light-colored, loose-fitting, and long-sleeved clothing. Also, protect their eyes and faces by using wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Use Sunscreen: It is important to use sunscreen for babies over 6 months old and children. The sunscreen should have a minimum SPF of 30 and provide broad-spectrum protection (blocking UVA and UVB). Apply the sunscreen at least 20 minutes before going outside and reapply every 2 hours.
- Ensure Sufficient Fluid Intake: On sunny days, make sure your children drink an adequate amount of fluids. Support their hydration with water, fruit juices, or watery foods. Fluid loss occurs faster under the sun, so it is important for children to drink water frequently.
- Provide Treatment for Sunburns: If your child gets a sunburn, you can apply cold compresses or use sunburn creams for mild burns. For severe burns, you may need to consult a healthcare professional.
Remember, children's skin can be affected by sun rays they are exposed to over many years. Protecting them from the harmful effects of the sun is important for healthy skin and a future with reduced risks.
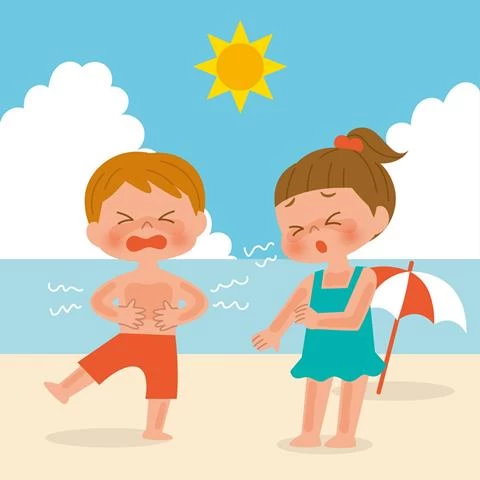

What Should You Do First for Children Exposed to Heatstroke?
Heatstroke is a serious condition that occurs as a result of excessive exposure to the sun, requiring prompt intervention. Here are the first steps to take for a child exposed to heatstroke:
- Immediately Move to a Shaded Area: Move a child showing signs of heatstroke to a shaded area away from the sun. Prefer a cool and well-ventilated place.
- Ensure Fluid Intake: Heatstroke can cause fluid loss and dehydration in the body. Provide immediate fluid replenishment to the child. Prefer water or electrolyte-containing beverages. However, if the child has symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, do not force them to drink water and consult a healthcare professional immediately.
- Keep the Body Cool: Take cooling measures to lower the child's body temperature. Moisturize their body with water and keep them in a cool environment. You can gradually reduce body temperature by using a cold shower or wet towel.
- Apply Methods to Alleviate Discomfort: You can apply a cool cloth to the child's head and neck to alleviate discomfort. Provide a quiet environment for the child to feel comfortable in case of headaches or restlessness.
- Seek Urgent Medical Assistance: If the child's condition rapidly worsens or they show severe symptoms (loss of consciousness, fainting, severe headaches, vomiting, seizures), seek immediate medical assistance. Heatstroke is a serious condition and may require professional help.
An important point is to ensure that the child does not get exposed to the sun again after heatstroke. Protect your child from the harmful effects of the sun by using sun-protective clothing, hats, and sunscreen. Additionally, help them maintain fluid balance by regularly ensuring their fluid intake.
Heatstroke is a serious condition and poses a significant health risk. Therefore, limiting the duration of sun exposure, taking preventive measures, and intervening quickly and effectively when heatstroke symptoms occur are of great importance.
Wishing you healthy days!