Scabies: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
- Scabies: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
- What is Scabies?
- Ways of Spreading Scabies
- Symptoms of Scabies
- Treatment of Scabies
- Prevention of Scabies
- Conclusion
Scabies is a contagious skin disease that causes itching and redness. This condition is caused by a microscopic parasite named Sarcoptes scabiei and is widespread globally. Scabies is an infection that is transmitted through direct contact between individuals and tends to spread in crowded places, communal living spaces, or through sexual contact.
What is Scabies?
Scabies is an infectious skin disease caused by microscopic parasites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These parasites burrow into the upper layers of the skin, laying their eggs and secreting enzymes that, upon larval development, lead to itching, redness, blisters, and rashes on the skin.
Ways of Spreading Scabies
Scabies is typically transmitted through direct person-to-person contact, but various factors and pathways can also play a role in its spread. Here are the ways scabies can spread:
- Direct Skin Contact: The most common transmission method is through direct contact with an infected person's skin. This contact often occurs among close relationships, family members, friends, or sexual partners, where scabies parasites can pass directly from one person's skin to another's.
- Shared Clothing and Personal Items: Wearing the clothes of an infected person or using their personal items like towels and bed linens can lead to the spread of scabies. Therefore, it is important for infected individuals not to share personal items with others.
- Communal Living Spaces: Scabies can rapidly spread in communal living spaces, especially in crowded environments such as schools, dormitories, prisons, and military units, increasing the risk of transmission.
- Sexual Contact: Scabies can also be transmitted through sexual contact, with a higher risk of transmission between sexual partners. Therefore, taking protective measures and limiting contact with a partner suspected of being infected is crucial.
- Healthcare Environments: Healthcare facilities and care homes may pose a risk of scabies transmission. Therefore, healthcare professionals need to adhere to hygiene protocols and take precautions when dealing with scabies-infected patients.
Scabies is more likely to spread in situations where cleanliness and personal hygiene habits are lacking. Adhering to cleanliness rules and personal hygiene measures can reduce the risk of scabies transmission.
Symptoms of Scabies
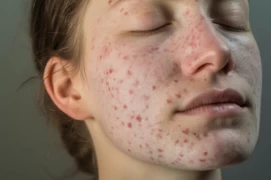
Symptoms of scabies typically manifest as itching, redness, blisters, and rashes on the skin. These symptoms usually appear 2 to 6 weeks after the onset of the infection. Here are the symptoms of scabies:
- Itching: The most common symptom of scabies is itching, which usually begins in thin areas of the skin, such as between the fingers, wrists, inner elbows, buttocks, genital area, and nipples. It intensifies, particularly at night.
- Redness: The infected areas of the skin become red, often accompanying itching and spreading over time.
- Blisters and Rashes: Due to scabies parasites burrowing into the upper layers of the skin, blisters, small red dots, or rashes may develop in these areas. These rashes are often found along the tunnels and folds of the skin.
- Tunnels: The traces of tunnels created by scabies parasites may be visible on the skin. These tunnels typically appear as thin, gray, or brown lines and are associated with the rashes on the skin.
- Intense Itching: Scabies itching can be extremely intense and bothersome, especially at night when body temperature rises, and the parasites are actively moving.
Scabies symptoms generally appear in the infected areas of the skin, but without proper treatment or if treatment fails, they can spread to a larger area.
Treatment of Scabies
Effective treatment of scabies requires accurate diagnosis. Scabies is typically treated with topical medications. Antiparasitic drugs such as permethrin and ivermectin are commonly used to kill scabies parasites. Additionally, cleaning the clothes and bedding of infected individuals plays a significant role in preventing further spread.
Prevention of Scabies
Maintaining cleanliness and hygiene measures is crucial for preventing scabies. Washing the belongings and clothes of infected individuals regularly, frequent handwashing, and exercising caution in close contact situations can help prevent the spread of scabies. Moreover, implementing necessary precautions in communal living spaces where scabies cases are present is essential.
Conclusion
Scabies is a contagious skin disease characterized by symptoms such as itching and redness. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are critical for controlling the disease. To prevent the spread of scabies, it is important to pay attention to personal hygiene and cleanliness habits, limit close contact with infected individuals, and ensure the correct application of scabies treatment. Dermatology experts continue to provide the best service to their patients by staying updated on current information related to scabies.
Sp. Dr. Yüksel Oltulu
Dermatology Specialist