About Periimplantitis
- About Periimplantitis
- What is Periimplantitis?
- Causes of Periimplantitis
- Diagnosis of Periimplantitis
- Treatment of Periimplantitis
- Prevention of Periimplantitis
- Conclusion
As a periodontology specialist, one of my most important responsibilities is to protect and maintain the health of the supporting structures of teeth. One of the biggest challenges we encounter in implant dentistry is a condition known as periimplantitis. This inflammatory condition affects the tissues surrounding dental implants and can lead to serious complications if not properly diagnosed and treated. In this article, I will discuss in detail what periimplantitis is, its causes, diagnostic methods, treatment processes, and preventive measures.
What is Periimplantitis?
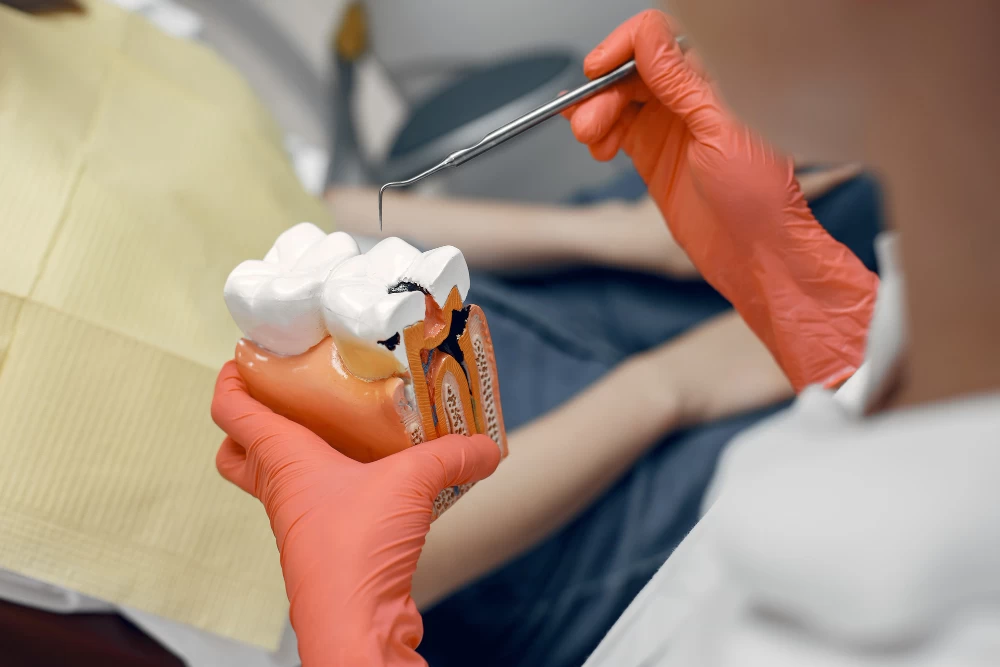
Periimplantitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the soft and hard tissues surrounding dental implants. This condition leads to the loss of supporting bone and jeopardizes the stability of the implant. Periimplantitis is similar to periodontitis, which affects the tissues around natural teeth. However, treating periimplantitis can be more complex because the tissues around implants have a different biological structure compared to natural teeth.
Causes of Periimplantitis
The primary causes of periimplantitis include:
- Bacterial Plaque and Biofilm: Similar to gum diseases, periimplantitis usually develops due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque and biofilm on the implant surface as a result of inadequate oral hygiene.
- Surgical Techniques and Procedures: The surgical techniques and procedures used during implant placement can affect the healing of surrounding tissues and lead to inflammation.
- Implant Surface and Design: The surface properties and design of implants can influence bacterial accumulation and biofilm formation. Rough surfaces may allow bacteria to adhere more easily.
- Systemic Factors: Systemic factors such as diabetes, smoking, and a weakened immune system can increase the risk of periimplantitis.
- Occlusal Trauma: Excessive forces applied to implants can lead to inflammation and bone loss in the surrounding tissues.
Diagnosis of Periimplantitis
Early diagnosis of periimplantitis is critical for successful treatment. Diagnosis is typically made through clinical examination and radiographic evaluation. Symptoms include:
- Gum Bleeding and Swelling: Bleeding and swelling of the gums around the implant are common symptoms.
- Deep Pocket Formation Around the Implant: Measurements made with a periodontal probe can reveal deep pocket formation.
- Bone Loss: Radiographic images may show bone loss around the implant.
- Pus and Discharge: The presence of pus and discharge around the implant may indicate infection.
- Mobility: In advanced cases, implant mobility may be observed.
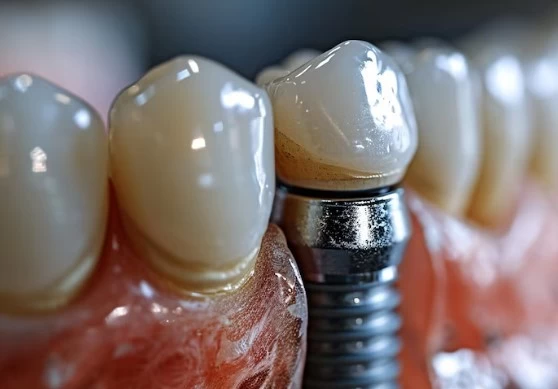
Treatment of Periimplantitis
The treatment of periimplantitis varies depending on the severity of the disease. Treatment options include:
- Mechanical Cleaning: Mechanical removal of plaque and biofilm from the implant surface forms the foundation of periimplantitis treatment. This cleaning is performed using ultrasonic devices and special hand instruments.
- Antimicrobial Therapy: Antibiotic and antiseptic agents are used to control the infection. Both local and systemic antimicrobial therapies can be applied.
- Surgical Intervention: In advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Infected tissues are removed through surgery, and bone loss may be repaired using bone grafts.
- Laser Therapy: Lasers can be effective in removing infected tissues and eliminating bacterial biofilm. Laser therapy is preferred as a minimally invasive method.
- Regenerative Procedures: In cases of advanced bone loss, bone grafts and biomaterials may be used to achieve bone regeneration.
Prevention of Periimplantitis
Preventing periimplantitis is vital for the long-term health and longevity of dental implants. Preventive measures include:
- Regular Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing around the implant are critical to preventing plaque accumulation.
- Periodic Professional Cleaning: Regular check-ups and professional cleanings by a dentist reduce the risk of periimplantitis.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking increases the risk of periimplantitis. Therefore, quitting smoking is important.
- Balanced Diet and Systemic Health: A balanced diet and control of systemic diseases reduce the risk of periimplantitis.
- Control of Occlusal Forces: Regular monitoring of occlusal forces to prevent excessive force on the implants is important.
Conclusion
Periimplantitis is a serious condition that threatens the success of dental implants. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the progression of periimplantitis can be halted, and the health of the implants can be preserved. As a periodontology specialist, our priority is to protect the health of the tissues around our patients' implants and to offer the best treatment approaches to prevent periimplantitis. We must not forget that regular oral care and professional dental check-ups are essential for maintaining healthy implants and long-lasting smiles.
Wishing you healthy days,

Prof. Dr. Elif EservAcarel
Periodontology Specialist