Expert Touch on Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Pain Management
- Expert Touch on Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Pain Management
- The Role of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation, and Joint Injections (Prolotherapy) in TMJ Pain Management
- Causes of TMJ Pain
- Management of TMJ Pain
- Joint Injections: Prolotherapy and Neural Therapy
- Conclusion
The Role of Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation, and Joint Injections (Prolotherapy) in TMJ Pain Management
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) pain is a common health issue that can significantly affect patients' quality of life. The TMJ plays a critical role in daily functions such as chewing, speaking, and swallowing. In this article, I've discussed how TMJ pain can be managed using physical therapy and rehabilitation methods as well as joint injections (prolotherapy).
Causes of TMJ Pain
TMJ pain can result from various factors, including:
- Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD)
- Trauma or injuries
- Teeth clenching or grinding (bruxism)
- Stress and anxiety
- Joint inflammations (arthritis)
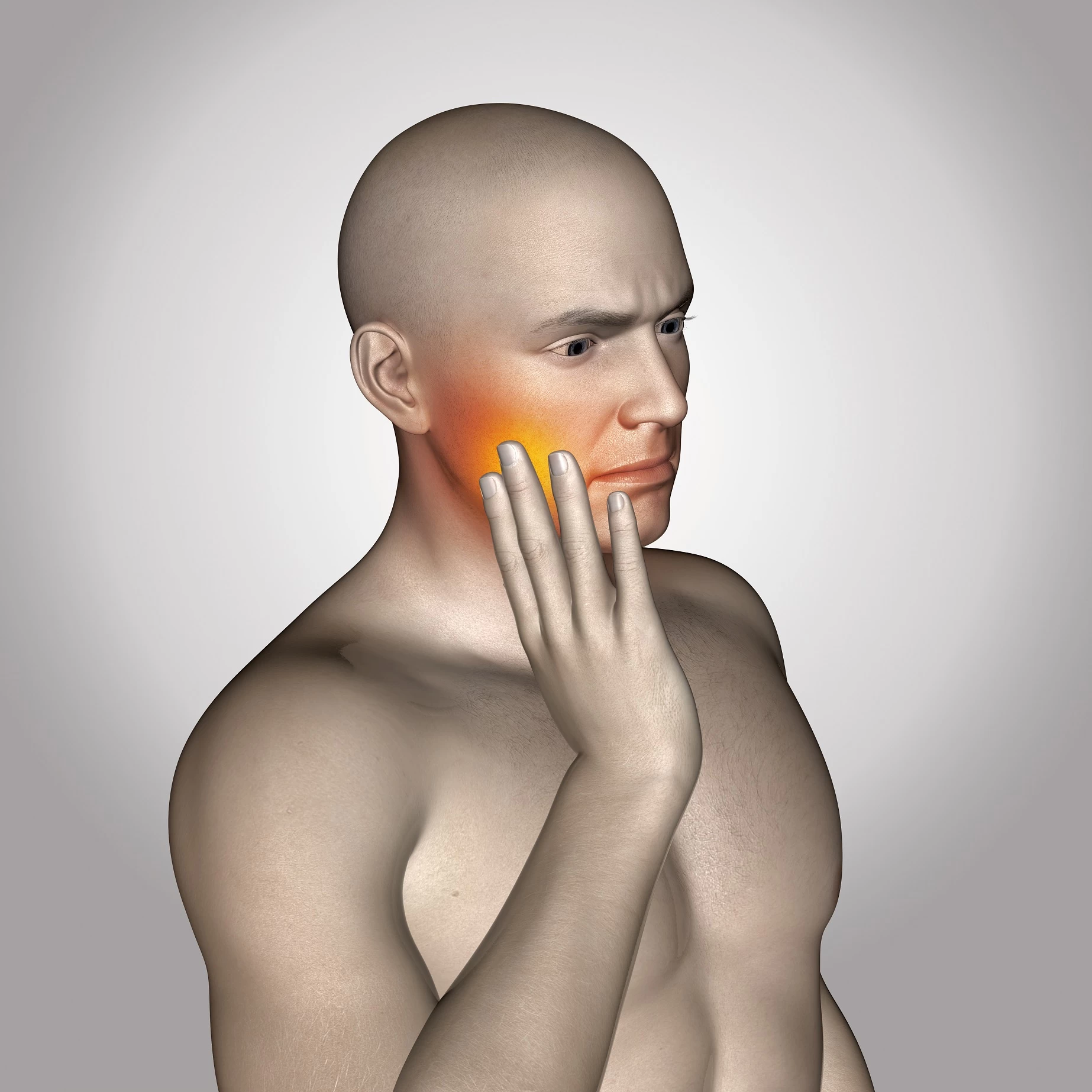
Management of TMJ Pain
Physical therapy and rehabilitation play a crucial role in managing TMJ pain. Some of these methods include:
- Exercises: I recommend various exercises to strengthen the TMJ and increase its range of motion. These exercises help enhance the flexibility and endurance of the jaw muscles. Isometric exercises are techniques we use to strengthen the jaw muscles and reduce pain.
- Manual Therapy: Osteopathic manual therapy involves specific techniques applied by physiatrists to mobilize the TMJ and surrounding muscles. These techniques effectively increase joint mobility and reduce pain. Soft tissue mobilization and joint mobilization help reduce stiffness and pain in the TMJ.
- Hot and Cold Applications: We frequently use hot and cold applications to manage TMJ pain. Hot applications help relax the muscles and increase blood flow, while cold applications reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Electrotherapy: Methods like Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and ultrasound can help alleviate TMJ pain. These methods reduce muscle spasms and control pain.
Joint Injections: Prolotherapy and Neural Therapy
- Prolotherapy: An effective injection method we use to treat TMJ pain. This technique involves injecting irritant solutions, such as dextrose, into the joint to stimulate the regeneration of weakened connective tissues.
- Prolotherapy's Role in TMJ Pain: TMJ pain often results from weakened or damaged jaw muscles. Prolotherapy can be an effective treatment for such pain. The injected solutions create controlled inflammation in the target area, attracting healing cells to the site. This process helps regenerate weakened tissues and improve their function.
- Treatment Process and Success Rates: Prolotherapy is typically administered every 2-4 weeks, with a total of 4-6 sessions. The success of the treatment is closely related to proper patient selection, the expertise of the practitioner, and regular follow-up. Patients' adherence to recommendations and, if necessary, receiving physical therapy can enhance success rates.
- Neural Therapy: This therapy aims to regulate the nervous system and activate the body's own healing mechanisms by injecting local anesthetics around the nerves. It can be effective in pain management.
- Neural Therapy's Role in TMJ Pain: TMJ pain can result from weakened or damaged jaw muscles and surrounding areas. Neural therapy helps regulate the nervous system and accelerates the healing process. The injected local anesthetics help nerves return to their normal functions, reducing pain.
- Treatment Process and Success Rates: Neural therapy is typically administered every 2-4 weeks, with a total of 4-6 sessions. The success of the treatment is closely related to proper patient selection, the expertise of the practitioner, and regular follow-up. Patients' adherence to recommendations and, if necessary, receiving physical therapy can enhance success rates.
Conclusion
TMJ pain can be effectively managed using physical therapy and rehabilitation methods, as well as joint injections (prolotherapy). These treatment methods play an important role in improving patients' quality of life and helping them regain their daily functions. Creating an individualized treatment plan for each patient is crucial for achieving the best results.
Wishing you pain-free days...

Dr. Elif Berber
Specialist in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation