Perspectives on Cancer Pain Management by a Pain Specialist (Algologist)
- Perspectives on Cancer Pain Management by a Pain Specialist (Algologist)
- Causes of Cancer Pain
- Types of Cancer Pain
- Management of Cancer Pain
- Challenges in Cancer Pain Management
- Conclusion
Cancer pain is a challenging experience that significantly impacts the quality of life for patients and their families. As a Pain Specialist, I am fully aware of my role in managing this pain and improving the quality of life for my patients. Controlling cancer pain can help patients navigate their treatment journey more comfortably, both physically and psychologically. In this article, I will discuss in detail the causes, types, management strategies, and treatment approaches for cancer pain.
Causes of Cancer Pain
Cancer pain can arise from various causes due to the spread and growth of cancer cells. This pain may be directly related to the tumor itself or associated with the side effects of treatment processes. The common causes of cancer pain include:
- Tumor Growth and Pressure: As tumors grow, they can press on surrounding tissues, nerves, bones, or organs, causing severe pain. For example, a tumor located in the spine can compress nerve roots, leading to both localized and widespread pain.
- Bone Metastases: When cancer cells spread to the bones, they can cause severe and often unbearable pain. The weakening and fragility of the bone tissue can further exacerbate this pain.
- Surgery and Radiotherapy: Surgical and radiotherapy treatments used in cancer care can damage nerve tissues, leading to long-term pain. Such pain often becomes chronic during the post-treatment period.
- Chemotherapy: Side effects of chemotherapy, such as nerve damage (neuropathy), can cause symptoms like burning, tingling, or constant pain, especially in the hands and feet.
Types of Cancer Pain
Cancer pain can be classified based on its type and severity. Three main types of pain are typically identified:
- Somatic Pain: This type of pain originates from the skin, muscles, bones, or joints. It is usually well-localized and constant. For example, pain related to bone metastases falls into this category.
- Visceral Pain: This type of pain originates from internal organs and is usually dull, pressure-like, and widespread. Pain from organs in the abdominal area or structures within the chest are examples of visceral pain.
- Neuropathic Pain: Neuropathic pain results from nerve damage and is often described as a burning, tingling, or electric shock-like sensation. It is frequently observed after cancer treatments.

Management of Cancer Pain
Managing cancer pain requires a multidisciplinary approach, and personalized treatment plans should be created based on the type, severity of the pain, the patient's overall health, and treatment goals. The main methods used in this process include:
- Pharmacological Treatment:
- Opioids: Opioids, such as morphine, oxycodone, and fentanyl, are strong pain relievers used for severe cancer pain. These medications can be very effective in controlling pain but must be used with caution due to potential side effects like dependency, constipation, and drowsiness.
- Non-Opioid Analgesics: Medications like acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used for mild to moderate pain and can also be combined with opioids.
- Adjuvant Medications: Adjuvant medications, such as antidepressants and anticonvulsants, are used to treat neuropathic pain. These drugs can help alleviate nerve pain.
- Invasive Interventions:
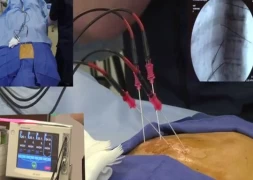
- Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks aim to stop the transmission of pain by targeting specific nerve groups. This method is particularly effective for localized pain.
- Epidural and Intrathecal Infusions: The direct application of certain pain medications to the area surrounding the spinal cord is used for persistent and widespread pain.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: In this method, specific nerve tissues are heated with radiofrequency waves to block pain transmission.
- Non-Pharmacological Treatments:
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Physical therapy can help improve patients' mobility, contributing to pain management. Additionally, techniques such as massage and hot/cold applications can help alleviate pain.
- Psychological Support: Psychological support plays a critical role in managing cancer pain. Developing strategies for coping with pain can improve patients' quality of life. Psychotherapy, relaxation techniques, and meditation can be beneficial in this process.
Challenges in Cancer Pain Management
Managing cancer pain can sometimes present challenges. Factors such as patients' individual pain thresholds, responses to medications, and psychological conditions play a significant role in this process. Additionally, the risk of opioid dependence may cause patients to be hesitant about using pain medications. In such cases, communication between the patient and the doctor is crucial. Patients' concerns should be addressed, and regular follow-up should be conducted throughout the treatment process.
Conclusion
Cancer pain management is a complex and meticulous process. As a Pain Specialist, my goal is to enhance my patients' quality of life by creating personalized treatment plans to minimize their pain. Effective control of cancer pain allows patients to experience their treatment journey more comfortably, both physically and emotionally, and increases their adherence to treatment. In the fight against cancer, effective pain management helps patients face this challenging process with greater strength and hope.

Assoc. Prof. Tülin Arıcı
Pain Specialist (Algologist)