Pneumonia: The Silent Enemy of the Lungs
- Pneumonia: The Silent Enemy of the Lungs
- What is Pneumonia?
- Symptoms of Pneumonia
- Risk Factors
- Diagnosis and Diagnostic Methods
- Treatment Methods
- Supportive Therapies:
- Preventive Measures Against Pneumonia
- Conclusion
Hello, As a Pulmonology Specialist, I would like to provide information about pneumonia, a serious disease known in medical literature as "pneumonia," which leads to an infection in the lung tissue. This disease affects millions of people every year and poses a significant risk, especially for children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
In this article, I will present a comprehensive guide covering all aspects of pneumonia, from its symptoms to preventive measures.
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs, often caused by an infection. These alveoli fill with fluid or pus, making oxygen exchange difficult and leading to breathing problems. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens.
Common Causes:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: The most common cause is Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Viral Pneumonia: Viruses such as influenza and COVID-19 are primary culprits.
- Fungal Pneumonia: More prevalent in individuals with compromised immune systems.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the severity of the infection, the patient's age, and immune status. Common symptoms include:
- High fever and chills
- Severe cough: May be productive (with mucus) or dry
- Shortness of breath: Noticeable even with mild activities
- Chest pain: Especially aggravated by breathing or coughing
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bluish lips or nails: Indicating oxygen deficiency
In children and the elderly, symptoms may differ. For instance, children may show rapid breathing and loss of appetite, while confusion might be a notable symptom in older adults.
Risk Factors
While pneumonia poses a risk to everyone, certain groups are more susceptible:
- Age: Children under 2 years and adults over 65 years.
- Weakened immune systems: Conditions like cancer, HIV, or post-organ transplantation.
- Chronic diseases: COPD, asthma, heart failure, diabetes.
- Smoking and alcohol use: Weakens the lungs' defense mechanisms.
- Hospital settings: Prolonged hospital stays can lead to hospital-acquired pneumonia, often caused by resistant microorganisms.
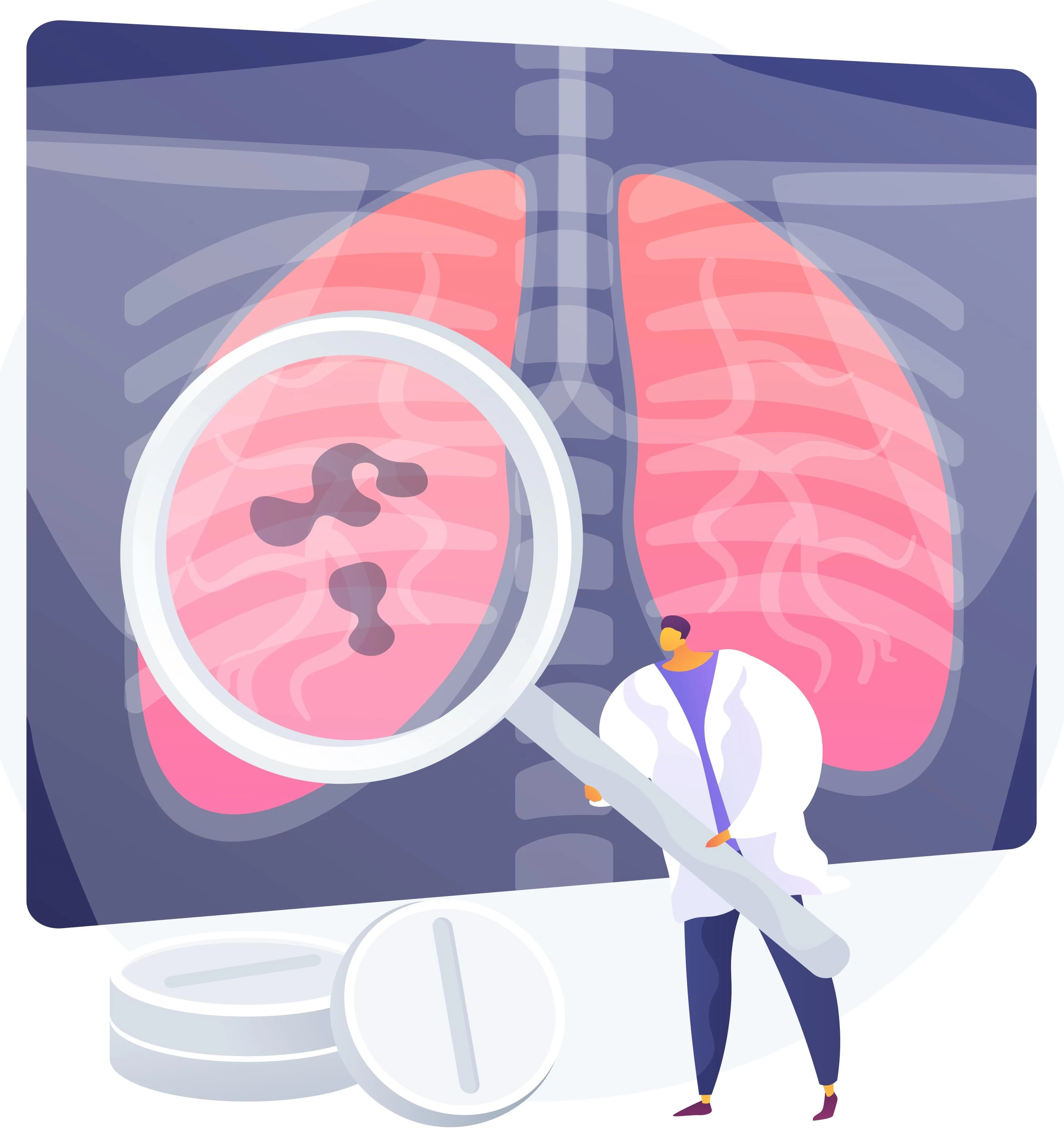
Diagnosis and Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing pneumonia involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various tests:
- Physical examination: Abnormal lung sounds such as crackles or wheezes may be detected using a stethoscope.
- Chest X-ray: Helps visualize inflamed areas of the lungs.
- Blood tests: Assess the severity and type of infection.
- Sputum culture: Identifies the causative organism.
- Pulse oximetry: Measures blood oxygen levels.
Treatment Methods
The treatment of pneumonia depends on the underlying cause and severity of the disease:
- Bacterial Pneumonia: Treated with antibiotics prescribed by a physician.
- Viral Pneumonia: Antibiotics are ineffective. Rest, fluid intake, and sometimes antiviral medications are recommended.
- Fungal Pneumonia: Managed with antifungal drugs.
Supportive Therapies:
- Antipyretics and pain relievers
- Adequate fluid intake
- Oxygen therapy for patients experiencing respiratory distress
Preventive Measures Against Pneumonia
Although pneumonia is a serious illness, it can largely be prevented by taking the following precautions:
- Vaccination:
- Pneumococcal vaccine: Provides effective protection against bacterial pneumonia.
- Influenza vaccine: Reduces the risk of viral infections leading to pneumonia.
- Hand hygiene: Regular handwashing prevents the spread of bacteria and viruses.
- Smoking cessation: Improves lung immunity.
- Strengthening the immune system: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep support immune health.
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a disease that can be largely controlled with early diagnosis and proper treatment. However, if neglected, it can lead to severe complications. As a Pulmonology Specialist, I encourage individuals, particularly those in high-risk groups, to be aware of pneumonia symptoms and prioritize regular health check-ups.
Let us remember that protecting our lungs is a critical step toward a healthy life. If you experience any symptoms, do not hesitate to consult a specialist. Wishing you a healthy and fulfilling life...

Dr. Aziz Uluışık
Pulmonology Specialist