Chronic Otitis Media - Part 1: Definition, Causes, and Symptoms
- Chronic Otitis Media - Part 1: Definition, Causes, and Symptoms
- What is Chronic Otitis Media?
- Factors Contributing to Chronic Otitis Media
- Symptoms of Chronic Otitis Media
Chronic otitis media is a chronic condition resulting from inflammation of the middle ear, which can also lead to hearing loss. In the first part of my three-part article on chronic otitis media, we will explore the definition of the disease, its contributing factors, and the symptoms.
What is Chronic Otitis Media?
Chronic otitis media is a condition characterized by prolonged inflammation in the middle ear, where recurrent infections are frequently observed. This condition is typically marked by the perforation of the eardrum and can result in hearing loss. Chronic otitis media often develops when acute otitis media (ear infection) is left untreated or becomes recurrent.
Factors Contributing to Chronic Otitis Media
Several factors contribute to the development of chronic otitis media, often arising from repeated infections or untreated infections in the middle ear. Here are some factors that can lead to chronic otitis media:
- Acute Otitis Media (AOM): Acute otitis media is a sudden infection of the middle ear. If this infection is not effectively treated or recurs persistently, it can lead to the development of chronic otitis media.
- Recurrent Otitis Media Attacks: Frequent occurrences of middle ear infections, especially in children, can contribute to the development of chronic otitis media and increase the risk of chronicization.
- Eardrum Perforation: If the eardrum is perforated, it allows easier access for microbes and bacteria to reach the middle ear, leading to infection and posing a risk for chronic otitis media.
- Changes in Air Pressure: Sudden changes in air pressure, especially in frequent flyers or divers, can increase the risk of inflammation in the ear and the development of chronic otitis media.
- Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system reduces the body's ability to fight infections. This vulnerability can lower resistance to middle ear infections and increase the risk of chronic otitis media.
- Secondhand Smoke and Air Pollution: Passive smoking and air pollution can increase inflammation in the middle ear and contribute to the development of chronic otitis media.
- Genetic Factors: Familial predisposition has shown that some individuals may be more susceptible to middle ear infections due to genetic factors, increasing the risk of chronic otitis media.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can increase the risk of chronic otitis media by causing congestion and fluid accumulation in the middle ear.
The combination of these factors influences the likelihood of individuals developing chronic otitis media. Individuals with suspected chronic otitis media should consult an ear, nose, and throat specialist to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
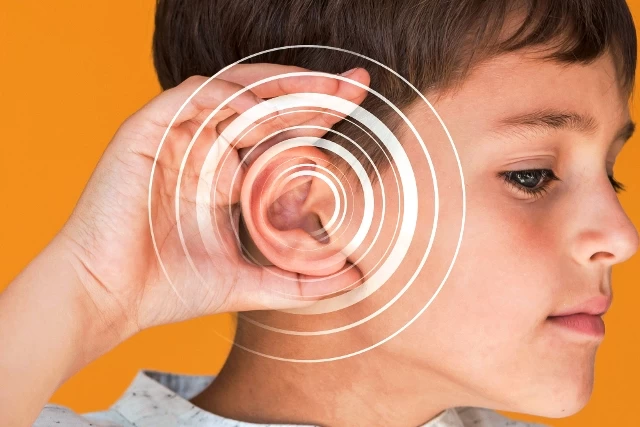
Symptoms of Chronic Otitis Media
Chronic otitis media is a condition where inflammation in the middle ear persists, and recurrent infections are common. While symptoms may vary from person to person, the following are commonly observed:
- Hearing Loss: Chronic otitis media typically results in hearing loss. Inflammation and fluid accumulation affect the normal functioning of the middle ear, leading to decreased hearing ability.
- Ear Discharge: Ear discharge, often yellow, green, or bloody, is a common symptom of chronic otitis media, indicating ongoing infection.
- Sensation of Fullness in the Ear: A feeling of fullness, pressure, or blockage in the ear is a common symptom of chronic otitis media, resulting from fluid accumulation or inflammation in the middle ear.
- Tinnitus: Chronic otitis media can cause tinnitus, where individuals perceive sounds such as ringing, buzzing, or roaring in the ears.
- Headache: Another symptom of chronic otitis media is headaches, attributed to inflammation or pressure in the ear.
- Balance Issues: Due to emerging hearing loss and inner ear problems, balance issues may arise, affecting coordination and balance control.
These symptoms typically manifest continuously or periodically and persist for an extended period.
In this first part of my three-part article on "Chronic Otitis Media," we have examined the definition of this ear condition, its contributing factors, and its symptoms. I look forward to meeting you in the next part.

Op. Dr. Selami Yavuz
Ear, Nose, and Throat Specialist





