
Gastroesophageal Reflux: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
- Gastroesophageal Reflux: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
- What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
- What Are the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux?
- What Are the Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux?
- What are the Treatment Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux?
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux?
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) is a digestive disorder that occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. Normally, a muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) separates the stomach from the esophagus and prevents the backflow of stomach contents. However, in individuals with GERD, this sphincter becomes weakened or relaxed, allowing stomach acid to reflux back into the esophagus.
GERD causes symptoms such as a burning sensation in the chest (heartburn) or a sour taste in the mouth. When the stomach contents come into contact with the walls of the esophagus, it can cause irritation and inflammation. Common symptoms of GERD include chest pain, difficulty swallowing, coughing, a sensation of something stuck in the throat, belching, and bad breath. These symptoms typically worsen after meals and can be exacerbated when lying down or bending over.
In this article, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and available treatment options for GERD.
What Are the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux?
The most common symptoms of GERD include:
• Heartburn: A burning sensation in the esophagus can occur due to the backflow of stomach acid. This is usually felt in the chest and intensifies after regurgitation of stomach contents.
• Acid regurgitation: Individuals with GERD may experience a sour taste in their mouth. This is a result of stomach contents refluxing into the esophagus.
• Chest pain: Chest pain caused by GERD can sometimes be mistaken for a heart attack. It typically presents as a burning or squeezing pain that worsens after meals.
• Difficulty swallowing: Some individuals with GERD may experience difficulty swallowing due to irritation of the esophagus. Narrowing or scarring of the esophagus can contribute to this symptom.
• Other symptoms: GERD can also cause symptoms such as coughing, belching, bad breath, a sensation of something stuck in the throat, and hiccups.
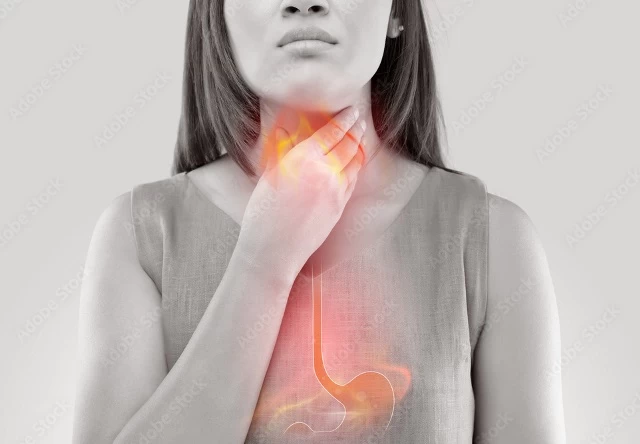
What Are the Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux?
Underlying causes of GERD include:
• Weakness of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES): The LES is a muscular structure that separates the stomach from the esophagus. When the LES becomes weakened or relaxed, it allows stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus.
• Motility disorders of the stomach: Normal peristaltic movements of the stomach help prevent GERD. Motility disorders of the stomach can increase the risk of stomach contents refluxing into the esophagus.
• Hiatal hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when a portion of the stomach protrudes into the chest cavity along with the esophagus. This condition can affect the function of the LES and lead to GERD.
• Diet and lifestyle factors: Consuming high-fat foods, chocolate, mint, caffeine, alcohol, and smoking can trigger GERD symptoms.
What are the Treatment Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux?
There are various treatment options for GERD:
• Lifestyle changes: Making dietary and lifestyle modifications can help reduce GERD symptoms. These changes include weight loss, staying upright after meals, sleeping with an elevated pillow, avoiding acidic and spicy foods, and abstaining from smoking/alcohol consumption.
• Medication therapy: Medications such as antacids, H2 receptor blockers, and proton pump inhibitors can alleviate symptoms by reducing stomach acid. It is important to use prescribed medications regularly and correctly.
• Surgical intervention: Surgical options may be considered when medication therapy or lifestyle changes are insufficient. One surgical procedure called fundoplication strengthens the connection between the stomach and esophagus, relieving GERD symptoms.
• Endoscopic treatments: GERD can also be treated using endoscopy. Endoscopic procedures can be performed with non-surgical methods to prevent the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) is a common digestive disorder that can significantly impact quality of life. Causes of GERD include weakness of the LES, motility disorders of the stomach, and hiatal hernia. Various treatment options are available, including lifestyle changes, medication therapy, surgical intervention, and endoscopic treatments. It is important for patients to consult with a gastroenterology specialist to alleviate GERD symptoms and prevent long-term complications.






