A Normal Menstrual Cycle: What Should The İntervals, Duration, And Amount Be?
- A Normal Menstrual Cycle: What Should The İntervals, Duration, And Amount Be?
- What Should The İntervals Of A Normal Menstrual Cycle Be?
- What Does İrregular Bleeding İnclude As A Definition?
- What Does Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding Mean?
- How Much Should The Menstrual Blood Flow Be?
- What is Spotting?
- What is Bleeding?
- What is Breakthrough Bleeding?
What Should The İntervals Of A Normal Menstrual Cycle Be?
Contrary to popular belief, the menstrual cycle encompasses the period from the first day of one menstrual bleeding to the first day of the next menstrual bleeding. In the first 2-3 years after the onset of menstruation (menarche), there can be irregular menstrual bleeding until hormonal balance is established. During this age range, a menstrual cycle of 21-45 days is considered normal. After this period, the menstrual cycle is considered normal if it falls within 24-38 days until menopause, which is defined as a period of 1 year without any menstruation. In the postmenopausal period, any occurrence of menstruation is considered pathological.
What Does İrregular Bleeding İnclude As A Definition?
The definition of irregular bleeding depends on the patient's age:
• 18 to 25 years: a difference in cycle length > 9 days
• 26 to 41 years: a difference in cycle length > 7 days
• 42 to 45 years: a difference in cycle length > 9 days
For patients younger than 18 or older than 45 years, the > 9-day definition is also applied, but the evidence defining what is normal is less clear in these groups.
What Does Prolonged Menstrual Bleeding Mean?
It is defined as menstrual bleeding that lasts continuously for more than 8 days; this is often but not always associated with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB).
How Much Should The Menstrual Blood Flow Be?
Traditionally, a menstrual cycle with a blood loss of 5-80 ml is considered normal when measurable methods are available. However, these methods are not practical, so an estimate is often made based on the patient's history and various bleeding patterns.
- If you have to change your pad every 2 hours
- If it causes symptoms such as dizziness, visual disturbances, or palpitations
- If it wakes you up from sleep at night
- If it leaks through your pad and onto your clothes, bed, or sheets
In these cases, excessive bleeding can be considered. However, this method has limited predictive power.
Calculating the bleeding amount using a scoring system can provide a more accurate assessment, with accuracy rates of 80-90%. Here is the menstrual bleeding table used for pad, tampon, and underwear calculation:
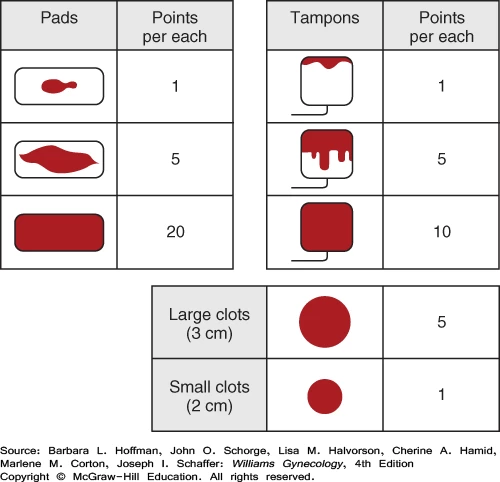
If the calculated score for bleeding days in one menstrual cycle is >100, it is defined as excessive menstrual bleeding (heavy menstrual bleeding).
What is Spotting?
It is defined as any bloody vaginal discharge that is not significant enough to require hygienic protection.
What is Bleeding?
Any bloody vaginal discharge that requires the use of protection such as pads or tampons is defined as bleeding.
What is Breakthrough Bleeding?
It is described as abnormal bleeding occurring between well-defined menstrual periods. Distinguishing breakthrough bleeding from irregular and/or very frequent menstruation can be difficult; therefore, this term should be used carefully before applying it to patients with other abnormalities. Inter-menstrual bleeding can be cyclic or non-cyclic.
Cyclical breakthrough bleeding: Approximately 9% of all women of reproductive age experience a small amount of bleeding in the mid-cycle during the mid-cycle period, which coincides with the ovulation period. This is thought to be related to the drop in circulating estrogen levels immediately after ovulation.
Non-cyclical inter-menstrual bleeding: Non-cyclic or unpredictable inter-menstrual bleeding is typically associated with non-malignant lesions such as chronic cervicitis/endometritis (inflammation of the cervix and uterine wall) or cervical or endometrial polyps (benign growths originating from the cervix or uterine wall), or intra-cavitary (within the uterine wall) uterine fibroids; bleeding after sexual intercourse is a common symptom. Less commonly, such bleeding may be indicative of a pathological process, such as cervical or endometrial (uterine wall) cancer.