Did You Have a Postmenopausal Bone Scan?
- Did You Have a Postmenopausal Bone Scan?
- What is Osteoporosis?
- The Importance of Postmenopausal Bone Density Screening in Women
- Preventive Measures Against Osteoporosis
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone density and weakening of the bone tissue. This condition makes the bones brittle and prone to fractures. It is characterized by the formation of holes in the internal structure of the bones and thinning of the bone tissue due to decreased bone mineral density.
Osteoporosis is often associated with aging because bone density decreases with age. In postmenopausal women, the risk of osteoporosis increases due to hormonal changes. When estrogen hormone levels decrease, bone loss can accelerate. However, osteoporosis can also occur in men, especially due to aging, hormonal changes, low testosterone levels, or certain health conditions.
Osteoporosis generally does not cause noticeable symptoms and is known as a "silent disease." In advanced cases, the tendency to easily fracture bones increases. Symptoms such as postural abnormalities like kyphosis (hunchback), neck, back, or hip fractures, and lower back pain can be consequences of osteoporosis.
The Importance of Postmenopausal Bone Density Screening in Women
Postmenopausal osteoporosis screening in women is an important step in providing early diagnosis and treatment for osteoporosis. Hormonal changes, decreased estrogen levels, and bone loss can occur in postmenopausal women, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Therefore, regular screening during the postmenopausal period is important to maintain bone health and prevent potential bone fractures.
One of the most common methods used in postmenopausal osteoporosis screening is bone mineral density (BMD) measurement. This test helps assess the risk of bone fracture by measuring bone density. BMD measurement is typically performed using a screening method called dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). This test assesses the density of bones in the hip and spine regions to evaluate the risk of osteoporosis. DEXA scanning is a quick, painless, and low-radiation test.
Another method for osteoporosis screening is clinical risk assessment. This assessment takes into account various factors such as age, gender, family history, lifestyle factors, hormonal status, and medication use to determine a patient's risk of developing osteoporosis. Clinical risk assessment helps categorize patients into low, medium, or high-risk categories, which helps determine the need for further screening or treatment.
Postmenopausal osteoporosis screening in women is important to provide early diagnosis and reduce the risk of fractures. With early detection, it is possible to maintain bone health through appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes. An internist or women's health specialist can determine the most suitable method and frequency for postmenopausal osteoporosis screening.
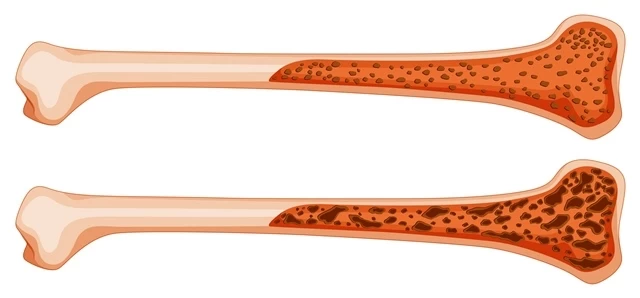
Preventive Measures Against Osteoporosis
Taking the following precautions is important to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and maintain bone health:
- Healthy eating: A balanced and nutritious diet is important for bone health. Following a dietary plan that includes foods rich in calcium and vitamin D, which support bone health, is important. Consuming calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables, fish, and nuts helps strengthen the bones. Vitamin D can be obtained through sunlight exposure, salmon, sardines, and vitamin D supplements.
- Regular exercise: Exercise is important for maintaining and strengthening bone health. Weight-bearing exercises, resistance training, and activities like walking can increase bone density. It is important to create an exercise program suitable for your age and health condition with the approval of your doctor.
- Avoidance of smoking and alcohol consumption: Smoking can accelerate bone loss and increase the risk of osteoporosis. Alcohol consumption can also negatively affect bone health. Therefore, it is important to avoid or limit smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Reducing the risk of falls: Falls are a significant risk factor for bone fractures. Taking fall prevention measures to create a safe environment at home is important. Measures such as preventing slippery floors, using fall-preventive lighting, having handrails on stairs, and wearing appropriate footwear can be taken. Additionally, balance and strengthening exercises can help reduce the risk of falls.
- Regular health check-ups: Individuals at risk of osteoporosis should regularly undergo health check-ups and follow screening methods such as bone density tests. This way, osteoporosis can be detected early, and a treatment plan can be established.
Remember, osteoporosis is a condition that can develop with age, but the risk can be reduced and bone health can be preserved through preventive measures and lifestyle changes.