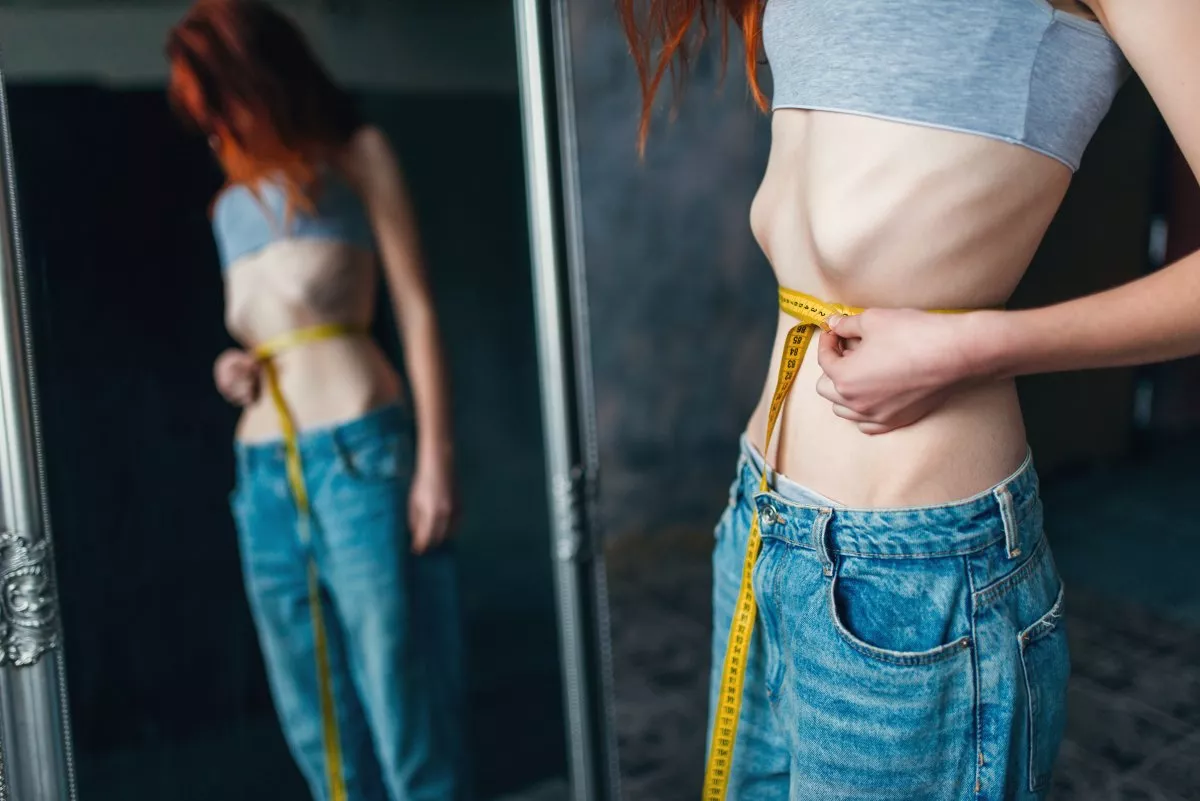
What is Anorexia Nervosa?
- What is Anorexia Nervosa?
- What symptoms does anorexia nervosa present with?
- What are the physical symptoms of anorexia?
- What emotional symptoms does anorexia nervosa have?
- When to go to the doctor?
- What are the risk factors for anorexia nervosa?
- What are the possible physical complications of anorexia?
- How to prevent anorexia?
- How is anorexia nervosa diagnosed?
- How is anorexia nervosa treated?
Anorexia nervosa is characterized by sub-normal weakness, fear of gaining weight, and an eating disorder. Even though they are extremely underweight, they continue to restrict seven foods in order not to gain or lose weight. They exercise excessively to continue losing weight and are afraid of gaining weight even though they are underweight. Anorexia is actually a disorder caused by emotional problems rather than an eating disorder. However, it is a dangerous way of dealing with emotional problems. You can cope with anorexia by eating a healthy diet.
What symptoms does anorexia nervosa present with?
- Extreme weakness when viewed physically, along with wanting to lose weight.
- Emotional problems, such as fear of getting fat.
- Sometimes people with anorexia hide themselves with their clothes and hide what they eat, so it is difficult to detect them.
- Physical symptoms
What are the physical symptoms of anorexia?
- Extreme weight loss
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Abnormal blood count
- Blue in the fingers
- Insomnia
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Breaking nails
- Hair loss
- Menstrual irregularity or absence of menstruation
- Pale Skin
- Constipation
- Heart rhythm disturbance
- Stomach ache
- Low blood pressure
- Swelling in the arms
- Swelling in the legs
What emotional symptoms does anorexia nervosa have?
- Not eating to avoid weight gain, so don't diet or fast
- Doing intense exercise
- Vomiting
- They cook for others, but do not eat them themselves
- Skipping meals or making excuses for not eating at all
- Chewing and spitting out
- Lying about eating
- Constant urge to weigh
- Fear of gaining weight
- Watching yourself in the mirror and thinking you're flawed
- Complaining of areas with obesity and fat
- Dress in layers
- Lack of emotion
- Being antisocial
- Not sleeping (Insomnia)
- Being nervous
When to go to the doctor?
A person with anorexia first of all does not see it as a disease and does not seek treatment. The desire to stay weak takes precedence over their health. If there is someone in your circle who you think has anorexia nervosa, persuade them to go to the doctor.
If you think you have one or more of the problems listed above, consult your doctor.
Why is anorexia nervosa diseased?
The exact cause of anorexia is not yet known. It is caused by biological, psychological and environmental factors.
- Biological. Some people may have this disease in their genes. But in which gene it is not known yet. Perfectionism is a trait that some people carry in their genes.
- Psychological. Anorexia Nervosa forces people on strict diets and not eating when they are hungry. They think they are never weak enough because they have perfectionism.
- Environmental factors. Western culture emphasizes that people should be weak. It equates factors such as being successful and valuable with weakness. Another is being weak among friends.
What are the risk factors for anorexia nervosa?
- Anorexia is mostly seen in women, but this rate has been increasing in men recently.
- Anorexia is more common among the young, but over the age of 40 it seems very rare. Conversations about weight among teens trigger these people.
- Genetic. Anorexia risk is sometimes carried through genes. People with a first-degree relative with an eating disorder are more at risk of anorexia.
- Diet. The onset of an eating disorder can sometimes be a diet. Hunger affects the brain and causes mental health to deteriorate, which manifests as anorexia.
- It becomes difficult to return to normal eating patterns.
- Emotional changes can cause anorexia along with stress. For example, job change, school change, separation from a spouse or lover, losing a loved one.
What are the possible physical complications of anorexia?
- Death. Even people with anorexia who are not overly thin can die because heart rhythm disturbance or disruption of fluid balance (electrolyte imbalance) can cause it.
- Muscle loss
- Bone loss
- Inability to menstruate
- Heart rhythm disorder
- Heart failure
- Bone fracture
- Testosterone reduction
- Swelling
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Kidney failure
- Kidney dysfunction
- All organs can be damaged, and even if the eating disorder improves in the future, it cannot be reversed.
- Possible mental anorexia
What are the complications?
- Mood disorder
- Personality disorder
- Alcohol and substance use
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders
- Suicide, self-harming tendency
How to prevent anorexia?
There is currently no way to prevent anorexia nervosa. If you think someone in your close circle has an eating disorder, talk to them about it, say that they can get help and that there are treatment options.
How is anorexia nervosa diagnosed?
If your doctor suspects anorexia nervosa, he or she will do some tests to see if the weight loss is due to other diseases.
These tests are:
- Physical examination. The ratio of height and weight is checked. He or she will also examine your blood pressure, heart rate, and lungs.
- Tests Complete blood count and more detailed tests can be done. A urine test may also be done.
- Evaluation of whether there are psychological problems. An eating disorder is tested by the specialist.
How is anorexia nervosa treated?
Anorexia is treated with the help of a group of specialists. These include mental health professionals, dietitians, and other internal medicine specialists.
What are the treatment difficulties in anorexia?
- Refuse treatment
- Thinking that no treatment is needed
- Thinking that anorexia is not a disease
- Afraid of gaining weight