What is Lupus (Butterfly Disease)? Symptoms and Treatment Methods
- What is Lupus (Butterfly Disease)? Symptoms and Treatment Methods
- What Are the Symptoms of Lupus?
- What Are the Causes and Risk Factors of Lupus?
- Types of Lupus:
- What Are the Complications of Lupus?
- How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
- How Is Lupus Treated?
Lupus is a chronic inflammatory disease that occurs when the immune system attacks the body's own tissues and organs. The inflammation caused by lupus can affect various body systems, including the joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. For an unclear reason, women are more likely to develop lupus than men.
There are four types of lupus: Systemic lupus erythematosus, Cutaneous lupus erythematosus, Drug-induced lupus, and Neonatal lupus. Systemic lupus erythematosus is the most common and most difficult of these four types.
In the past, lupus patients faced a miserable fate, but great progress and improvement has been made in the field of lupus diagnosis and treatment methods. Lupus patients today receive good treatments that enable them to lead effectively.
What Are the Symptoms of Lupus?
Lupus symptoms and signs may come on suddenly or develop slowly and gradually. Lupus cases are different, and no two lupus cases are the same.
Symptoms can be mild, severe, temporary or permanent. Most lupus patients suffer from episodes of the disease that last for varying durations; During this time, signs and symptoms worsen, then return to improvement and may disappear completely over a period of time.
Signs and symptoms vary depending on which organ in the body is affected. But these signs and symptoms often include:
- Tiredness
- Fever
- Being overweight or losing weight quickly
- Pain, stiffness and swelling in the joints
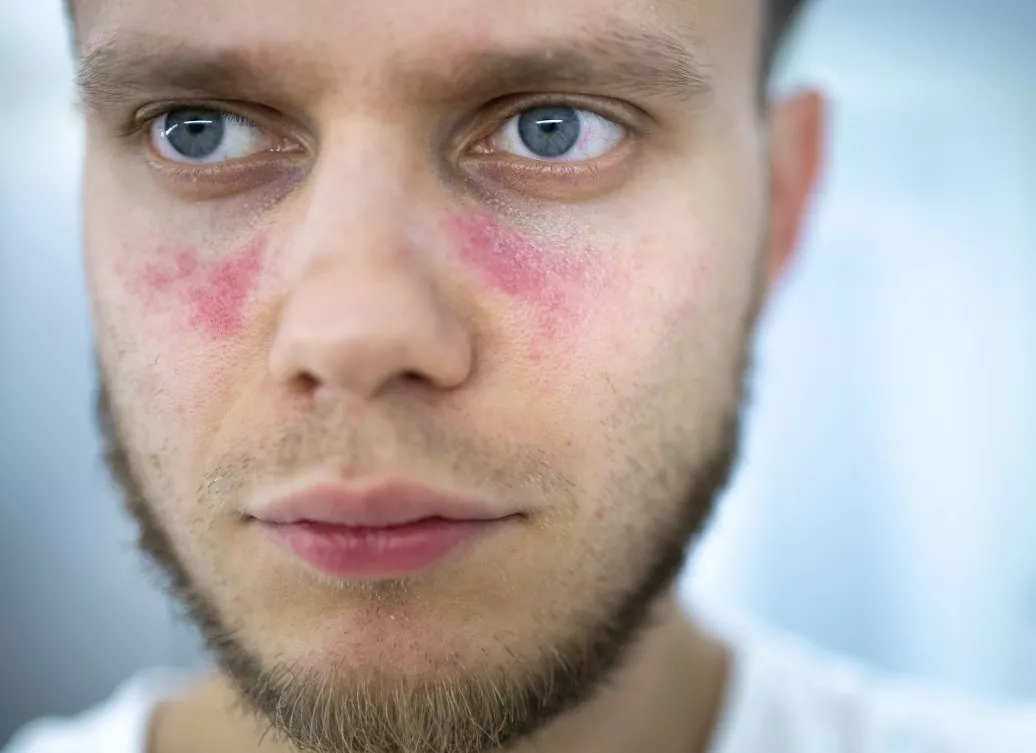
- A butterfly-shaped rash on the face covering the cheeks and bridge of the nose (Malar rash)
- Skin sores appear or aggravate as a result of sun exposure
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Raynaud's syndrome - fingers and toes on the hands and feet turn white or blue due to exposure to cold or during periods of great stress.
- Difficulty in breathing
- Chest pain
- Dry eyes
- Hypersensitivity to injuries
- Anxiety and depression
- Loss of memory
What Are the Causes and Risk Factors of Lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, meaning it occurs when the immune system attacks healthy tissues in the body instead of only attacking foreign bodies like germs and viruses. As a result, infections and damage occur in many parts/organs of the body, including the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain.
Until now, doctors do not know the true cause of autoimmune diseases such as lupus. It is believed that lupus is most likely caused by a combination of genetic factors and environmental factors. Doctors believe that a predisposition to lupus may be inherited, but not the disease itself. People with a genetic predisposition can develop lupus when exposed to an environmental agent that stimulates lupus, such as certain drugs or viruses.
Types of Lupus:
There are four types of lupus that are the same disease in terms of classification but have different characteristics and different treatments:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: Can affect any organ of the body.
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Affects only the skin.
- Drug-induced lupus: Occurs after using certain medications.
- Neonatal lupus: It is a rare type that affects newborns.
Doctors don't know what causes lupus, but they acknowledge a number of factors that can increase the risk of developing lupus, including:
- Gender: Lupus is more common among women than men.
- Age: Lupus can affect people at any stage of life, including infants, men, and the elderly, but it usually occurs in people between the ages of 15 and 45.
- Sunlight: Exposure to the sun can trigger the appearance of lupus-related skin lesions or cause an internal reaction in people susceptible to lupus.
- Some medications: Taking certain medications for a long time can cause lupus.
- Infection with Epstein - Barr virus - EBV.
What Are the Complications of Lupus?
The inflammation caused by lupus can affect many organs in the body, including:
- Kidneys
- Central nervous system
- Blood and blood vessels
- Lungs
- Heart
- Contamination (infection)
- Liver
- Bone tissue death (Osteonecrosis)
- Complications during pregnancy
How Is Lupus Diagnosed?
Lupus is difficult to diagnose because symptoms vary greatly from person to person. The signs and symptoms of lupus can change over time, and they can sometimes match the signs and symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, doctors consider this diagnosis only when signs and symptoms are more pronounced.
Even when the signs and symptoms are clear, lupus is difficult to diagnose because nearly all patients with lupus have frequent variations in the severity of the lupus. Sometimes the disease worsens, sometimes it disappears completely. The criteria established by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) for diagnosing lupus are:
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) has published a list of clinical and laboratory criteria that assist clinicians in diagnosing and classifying lupus. People who meet four of the 11 criteria at the same time or appear individually often have lupus. A doctor may consider this diagnosis even if some patients have fewer than four symptoms.
The defined criteria are:
- A facial rash that doctors call (Malar rash) is a butterfly-shaped rash that covers the bridge of the nose and spreads beyond the cheeks.
- A red, scaly rash called a 'discoid rash' that looks like a scaly patch on the skin.
- Sun-induced rash that occurs after exposure to sunlight
- Mouth sores that are not usually painful
- Pain and swelling in two or more joints
- Swelling of the membranes surrounding the heart and lungs.
- Kidney disease
- A neurological disorder such as convulsions or psychosis.
- Low blood counts such as low red blood cells, low thrombocytopenia, or low white blood cells (leukopenia)
- Positive ANA test results indicating the patient may have an autoimmune disease
- Positive results in the DNA antibody test, positive results in the SM-antibody test, positive results in the anticoagulant test, or positive results in other blood tests that may indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease as a false positive result in the syphilis test.
Laboratory tests:
To determine the diagnosis, the doctor may order the following blood and urine tests:
- Complete blood count
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
- Functioning of the liver and kidneys
- Urine test
- ANA - Antinuclear Antibody Test
- Chest X-Ray
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Syphilis test
How Is Lupus Treated?
Lupus treatment depends on signs and symptoms. Deciding on the symptoms, signs, and what type of medication to treat requires a careful assessment of preferences (advantages) versus risks (disadvantages) in consultation with a rheumatologist. When symptoms worsen or subside, the doctor and patient may decide together to switch medications or change the dose.
Common Lupus Medications:
There are three common types of medication to treat lupus if mild or moderate signs and symptoms are present. Treating acute lupus requires stronger and more effective medications. Generally, after an initial diagnosis of lupus, the doctor will discuss the following medications with the patient:
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs / NAIDs)
- Anti-malarial drugs
- Corticosteroids
Treating certain signs and symptoms of lupus. The type of treatment will be determined by the signs and symptoms. These treatments include:
- Treating painful and swollen joints
- Rash treatment
- Treat fatigue
- Treating swelling around the heart and lungs
Treatment of severe and severe cases of lupus:
Life-threatening cases of lupus include those that lead to kidney problems, central nervous system problems such as vasculitis and seizures. These may require more serious treatment. In such cases, the doctor and patient may consider using:
- High doses of corticosteroids
- Drugs that suppress the immune system
Clinical research:
Researchers are conducting clinical trials to develop new treatments for lupus. This research gives lupus patients a chance to try new treatments, but does not guarantee a cure. Treatments being investigated in clinical trials include:
- Stem cell transplant
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
- Rituximab (Rituxan)
- Alternative Treatments
Patients who fail to control all the symptoms of lupus with medication or who are tired and exhausted from lupus attacks may seek solutions in complementary medicine or alternative medicine. Recently, he notes, traditional physicians have begun to show more openness when discussing these possibilities with their patients. However, as only a small number of these treatments have been investigated in clinical trials, their efficacy in the treatment of lupus is difficult to predict, and the potential risks of these treatments in some cases remain unclear.
In all cases, patients interested in trying complementary or alternative therapies are advised to consult their physician first. It can help the doctor weigh the benefits against the risks and determine whether an alternative (or complementary) treatment might interfere with the effectiveness of the medication the patient is taking.
Complementary and alternative treatments common in the treatment of lupus include:
- Fish oil: Fish oil, as a food additive, contains omega-3 fatty acids that may benefit lupus sufferers.
- Flaxseed: Flaxseed contains alpha-linolenic acid, which can reduce inflammation in the body.