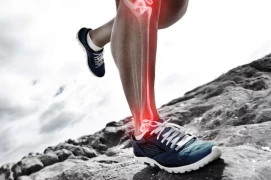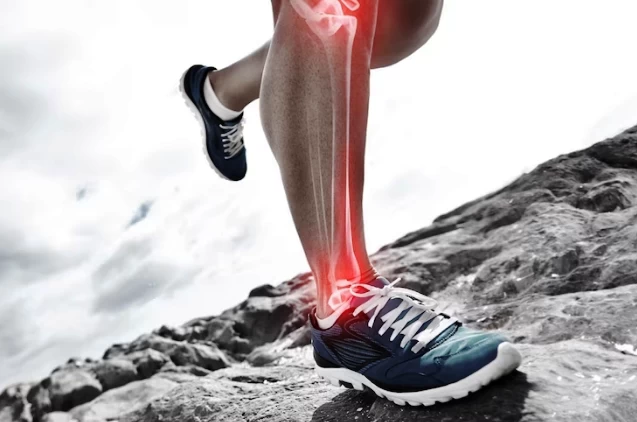
Ankle Cartilage Problems: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
- Ankle Cartilage Problems: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
- What Are Ankle Cartilage Problems?
- Causes of Ankle Cartilage Problems:
- Symptoms and Diagnosis Methods for Ankle Cartilage Problems:
- Treatment Options for Ankle Cartilage Problems:
The ankle is a complex joint that bears the weight of our body and provides flexibility and mobility during various activities. It comprises various structures, including cartilage, bones, ligaments, and muscles. Problems with ankle cartilage can arise due to disruptions or damage in the functions of these structures. In this article, I will cover general information on ankle cartilage problems, diagnosis methods, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What Are Ankle Cartilage Problems?
Ankle cartilage problems refer to damage, wear, or deterioration in the cartilage tissue of the ankle joint. The ankle joint is formed by the bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula) and the foot bone (talus). This joint is crucial for bearing body weight, maintaining balance, and allowing various movements.
Causes of Ankle Cartilage Problems:
Ankle cartilage problems can arise from various causes, often leading to damage, wear, or deterioration of the cartilage tissue. The common causes of ankle cartilage problems include:
- Trauma and Injuries: Trauma and injuries are among the most common causes of ankle cartilage problems. Falls, sports injuries, accidents, or impacts can result in damage to ankle cartilage. Cracks or tears in the cartilage surface may occur, especially when the joint is subjected to sudden and intense stress.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, continuous use, aging, and exposure to repetitive stresses can lead to wear and tear in the ankle joint. This can result in the loss of cartilage and deformities in the joint surface.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition affects an individual's cartilage health. Those with a family history of cartilage problems are more susceptible to such issues.
- Obesity: Being overweight increases the pressure on the ankle joint, accelerating wear and tear on the cartilage.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Connective tissue diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis can affect cartilage health, leading to ankle cartilage problems.
- Anatomical Anomalies: Congenital structural abnormalities or anatomical anomalies in the ankle joint can contribute to cartilage problems.
- Sports Injuries: Athletes, especially, may damage ankle cartilage due to repetitive movements, sudden turns, or excessive loading.
Ankle cartilage problems often result from a combination of these factors, and the specific causes may vary from person to person. Therefore, individualized treatment and management plans are essential, taking into account the unique circumstances of each patient.

Symptoms and Diagnosis Methods for Ankle Cartilage Problems:
Ankle cartilage problems manifest various symptoms. Below are common symptoms and diagnostic methods for ankle cartilage problems:
Symptoms:
- Pain: Ankle cartilage problems typically cause pain, often felt in the joint area during movement or specific activities throughout the day. The pain is commonly localized in the joint.
- Swelling: Cartilage damage can lead to inflammation around the joint, resulting in swelling in the ankle.
- Limited Range of Motion: Cartilage problems can restrict normal ankle movements, causing discomfort or pain during movement.
- Audible Clicking or Crunching Sounds: Cartilage damage can produce audible clicking, crunching, or friction sounds during joint movement.
- Night Pains: Many individuals experience increased pain due to ankle cartilage problems, especially during nighttime rest. This is often associated with the cumulative stress and load from daily activities.
Diagnosis Methods:
- Physical Examination: Healthcare professionals assess symptoms and conduct a physical examination to evaluate factors such as range of motion, swelling, tenderness, and stability.
- Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: Ankle X-rays are used to evaluate bone deformities, joint space gaps, and other signs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This imaging method provides detailed images, allowing better visualization of cartilage damage, soft tissues, and other details.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be ordered to evaluate conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or other inflammatory issues.
- Joint Fluid Analysis: Examining fluid within the joint can help identify inflammation, infection, or other problems.
- Radiological Imaging: In specific cases, other imaging methods such as computed tomography (CT) or ultrasound may be used.
Ankle cartilage problems are typically diagnosed through a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and imaging tests. Once diagnosed, an appropriate treatment and management plan is developed. Treatment options often depend on the severity and type of damage, as well as the overall health of the patient. Therefore, collaboration with a healthcare professional during the diagnosis and treatment process is crucial.
Treatment Options for Ankle Cartilage Problems:
The treatment of ankle cartilage problems may vary based on the severity, type, and overall health of the patient. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications to control pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility.
- Orthotics: Ankle supports or custom insoles to provide additional support.
- Injections: Injections that support cartilage repair (e.g., hyaluronic acid injections).
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions such as cartilage repair or joint replacement may be considered.
Preventive Measures for Ankle Cartilage Problems:
To prevent or reduce the severity of ankle cartilage problems, the following preventive measures can be taken:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in ankle-strengthening and flexibility exercises.
- Proper Footwear: Use supportive and properly fitting shoes that suit your foot structure.
- Protective Gear: Use appropriate protective gear when participating in sports activities.
- Healthy Nutrition: Maintain a balanced diet that includes nutrients essential for cartilage health.
In conclusion, ankle cartilage problems can encompass a wide range of issues, and the treatment approach is individualized. It is essential to seek medical attention when symptoms arise or if there is any suspicion of a problem. Collaborating with an orthopedic specialist during the diagnosis and treatment process is crucial for optimal outcomes.

op. Dr. Atakan Telatar
Orthopedic Surgeon