Gonarthrosis (Osteoarthritis of the Knee)
- Gonarthrosis (Osteoarthritis of the Knee)
- What is Gonarthrosis?
- Causes of Gonarthrosis:
- Symptoms of Gonarthrosis:
- Diagnosis of Gonarthrosis:
- Treatment Options for Gonarthrosis:
What is Gonarthrosis?
Gonarthrosis is a degenerative joint disease of the knee and a type of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a condition where the cartilage tissue in the joints deteriorates and wears down. Gonarthrosis specifically refers to the degeneration and weakening of the cartilage surface in the knee joint.
Cartilage in the knee joint covers the ends of the bones, enabling smooth and seamless joint movement. However, factors such as aging, excessive use, repetitive stress, joint injuries, or genetic predisposition can lead to the gradual wearing down of the knee cartilage. As the cartilage starts to deteriorate, friction increases during joint movement, leading to irritation and inflammation on the joint surfaces. Over time, this can result in symptoms such as knee pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Causes of Gonarthrosis:
The most common causes of gonarthrosis include:
- Genetic predisposition, which becomes more prominent with age.
- Joint fractures and injuries.
- Rheumatic diseases.
- Osteonecrosis, which occurs when bone cells around the joint die due to various reasons.
When combined with obesity, these factors can accelerate the progression of the disease and exacerbate the pain experienced by patients.
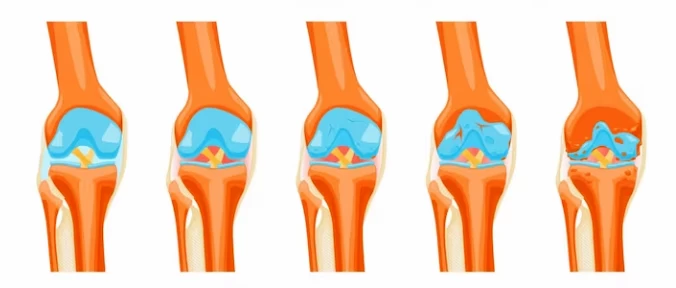
Symptoms of Gonarthrosis:
The symptoms of gonarthrosis arise due to the weakening and degeneration of the knee cartilage. The disease typically develops slowly and worsens over time. The following are common symptoms:
- Knee pain: Knee pain is one of the most prevalent symptoms of gonarthrosis. Initially, the pain may occur during joint movement or after physical activity and may ease with rest. However, as the condition progresses, the pain can become constant, even affecting the patient's sleep pattern.
- Knee stiffness: Individuals with gonarthrosis may experience difficulty in bending or straightening their knees. Stiffness is often felt, particularly in the morning or after prolonged periods of sitting.
- Knee swelling: Cartilage damage and inflammation in the knee joint can lead to swelling around the affected area.
- Restricted joint movement: As gonarthrosis advances, the range of motion in the knee joint may decrease. The knee's full movement can be restricted due to pain and damage to the cartilage surfaces.
- Audible and palpable joint friction: Patients with gonarthrosis may experience audible and palpable cracking or grating sensations in the knee joint during movement.
- Weakness in the surrounding muscles: Gonarthrosis can cause weakness in the muscles around the knee, affecting the knee's stability.
Symptoms can vary from person to person and may differ based on the stage of the disease, the individual's age, genetic predisposition, and other factors. If you are experiencing persistent symptoms such as knee pain, stiffness, or limited mobility, it is essential to consult a doctor for evaluation and accurate diagnosis. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate the effects of gonarthrosis.
Diagnosis of Gonarthrosis:
The diagnosis of gonarthrosis relies on the patient's medical history, physical examination, and X-ray imaging. In cases where there is a history of sports injuries or trauma in middle-aged patients, MRI of the knee may also be necessary to assess intra-articular structures.
Treatment Options for Gonarthrosis:
The treatment of gonarthrosis depends on its stage and the success of the chosen approach. In the early stages, lifestyle changes, the use of canes, and exercises can be beneficial. Pain relief can be achieved with the use of paracetamol-based painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. However, the long-term use of these drugs is known to cause kidney, liver, and gastrointestinal diseases.
For patients in the early and middle stages with no painful episodes, dietary supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin can be used to slow down cartilage deterioration and reduce pain. Hyaluronic acid injections into the knee joint (also known as viscosupplementation) and the application of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) from the patient's own blood into the knee joint have been found to be beneficial in this patient group.
In cases where surgery is not considered, or in patients with advanced gonarthrosis or acute painful episodes, knee intra-articular corticosteroid injections can be administered, with no more than one injection per month and no more than three injections per year. For patients in the early and middle stages without alignment issues, physical therapy can be effective in treating pain and loss of movement.
Surgical treatment options can be categorized under three main headings:
In patients with early and middle stages without alignment issues, the first surgical option involves arthroscopic removal of damaged cartilage and addressing any existing meniscal problems.In addition to arthroscopy, the second option consists of corrective osteotomy surgeries for patients with misalignment (malalignment) between the thigh and shin bones.In advanced cases, half or total knee replacement surgeries are high-success procedures.
It is essential to evaluate each patient individually to determine the most suitable treatment plan for them. The success of the treatment depends on early diagnosis, appropriate intervention, and patient compliance with the recommended management.