Hallux Valgus Syndrome
- Hallux Valgus Syndrome
- What is Hallux Valgus?
- Factors Leading to Hallux Valgus
- Symptoms of Hallux Valgus
- Treatment Options for Hallux Valgus
What is Hallux Valgus?
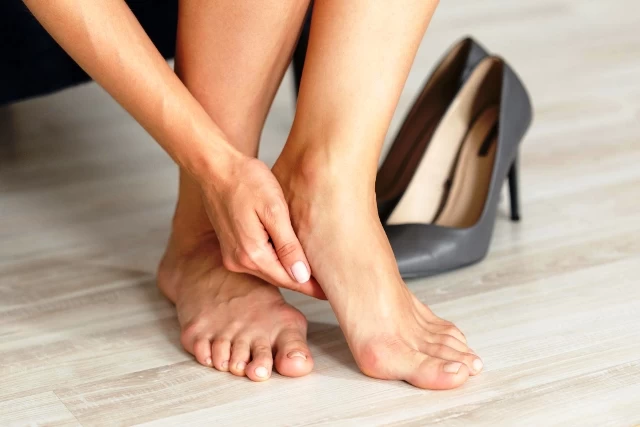
Hallux Valgus refers to a foot condition where the big toe deviates outward and creates a protrusion on the foot. In this condition, the big toe angles towards the other toes, and a bony prominence or swelling forms at the base of the big toe joint. This protrusion is also known as a "bunion."
Hallux Valgus develops due to structural abnormalities and joint issues in the foot. It is more commonly observed in women, often triggered by wearing high-heeled shoes, tight or ill-fitting footwear, or shoes that don't suit the foot structure.
Factors Leading to Hallux Valgus
Various structural, genetic, and lifestyle factors contribute to the development of Hallux Valgus. Some of these factors include:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of Hallux Valgus can increase susceptibility. Genetic factors play a role in the development of foot structure and joint abnormalities.
- Foot Structure: Structural features of the foot anatomy influence the risk of Hallux Valgus. Conditions like flat feet can increase susceptibility.
- Shoe Selection: Narrow or tight shoes, especially those with a narrow and pointed toe box, can exert pressure on the big toe and contribute to the development of Hallux Valgus. High-heeled shoes can also affect the ankle and foot structure, predisposing to the condition.
- Age: Hallux Valgus tends to become more common with age. As joints and connective tissues weaken over time, the risk of foot deformities increases.
- Gender: Hallux Valgus is more prevalent in women compared to men. This might be due to wider and more angled pelvic structure in women and the habit of wearing tight shoes.
- Rheumatic Conditions: Rheumatic diseases affecting joints and connective tissues can contribute to the development of Hallux Valgus.
- Foot Injuries and Stress: Foot injuries or prolonged stress can influence foot structure and trigger Hallux Valgus.
- Muscle Weakness: Weak foot and ankle muscles can reduce foot stability and increase the risk of Hallux Valgus.
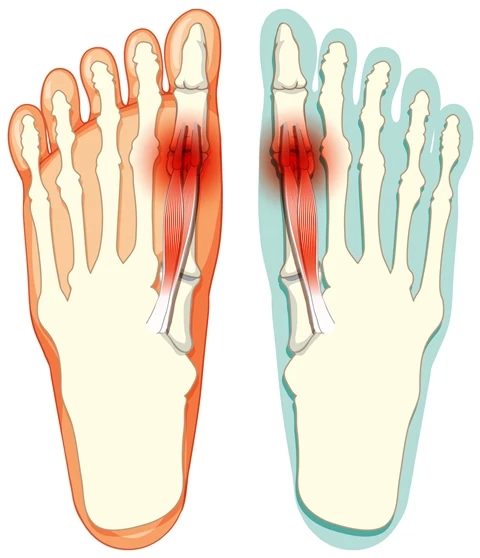
Symptoms of Hallux Valgus
Symptoms of Hallux Valgus may include:
- Swelling and Bony Prominence on the Big Toe: A protrusion or bony prominence can form at the base of the big toe joint, causing swelling and stiffness in the area.
- Pain and Sensitivity: Pain and sensitivity around the big toe region can be experienced, especially worsening after prolonged standing or walking.
- Stiffness in the Big Toe Joint: Stiffness and limited mobility can occur in the big toe joint, leading to difficulty in wearing shoes or moving the toes.
- Changes in Foot Shape: As the big toe deviates outward, deformities like hammer or claw toes can develop in other toes.
- Difficulty Wearing Shoes: Due to the protrusion and deformity of the big toe, wearing shoes can become uncomfortable and challenging.
- Foot Fatigue: Hallux Valgus can cause imbalance and improper weight distribution in the foot, leading to increased foot fatigue.
- Skin Issues: Friction and pressure on the big toe can result in irritation, redness, and corns on the skin.
These symptoms are commonly associated with Hallux Valgus, but individual experiences may vary, and the severity of symptoms can differ from person to person. If you are experiencing such symptoms or noticing changes in the shape of your big toe, consulting an orthopedic specialist is important for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can prevent progression or alleviate symptoms.
Treatment Options for Hallux Valgus
Treatment approaches for Hallux Valgus vary based on the severity of symptoms, age, activity level, and degree of foot deformity. Common treatment options include:
- Conservative Treatment:
- Shoe Modifications: Wearing comfortable shoes with a wide toe box can reduce pressure on the big toe and alleviate symptoms.
- Foot Orthotics: Custom orthotics or inserts can help correct foot structure and reduce pain.
- Pain Relievers and Anti-inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or medications recommended by a doctor can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy:
- Physiotherapy: Specific exercises and therapies can strengthen foot and ankle muscles, enhancing flexibility and stability.
- Injections:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the big toe joint can alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Orthotic Devices:
- Night Splints: Nighttime splints or braces can help maintain proper big toe alignment during sleep.
- Toe Spacers or Toe Separators: Devices that keep the big toe and other toes in correct alignment can be beneficial.
- Surgical Treatment: When conservative measures are ineffective or deformity is severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures aim to correct the big toe joint, perform bone realignment, and repair soft tissues. Surgery targets underlying structural issues and aims to improve symptoms. Post-surgery recovery may be required, and following the doctor's recommendations is crucial.
Remember that each patient's condition is unique, and the treatment approach should be tailored individually. Therefore, if you have Hallux Valgus symptoms, seeking guidance from an orthopedic specialist and receiving an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan is essential. Early intervention can help prevent progression or alleviate symptoms.



