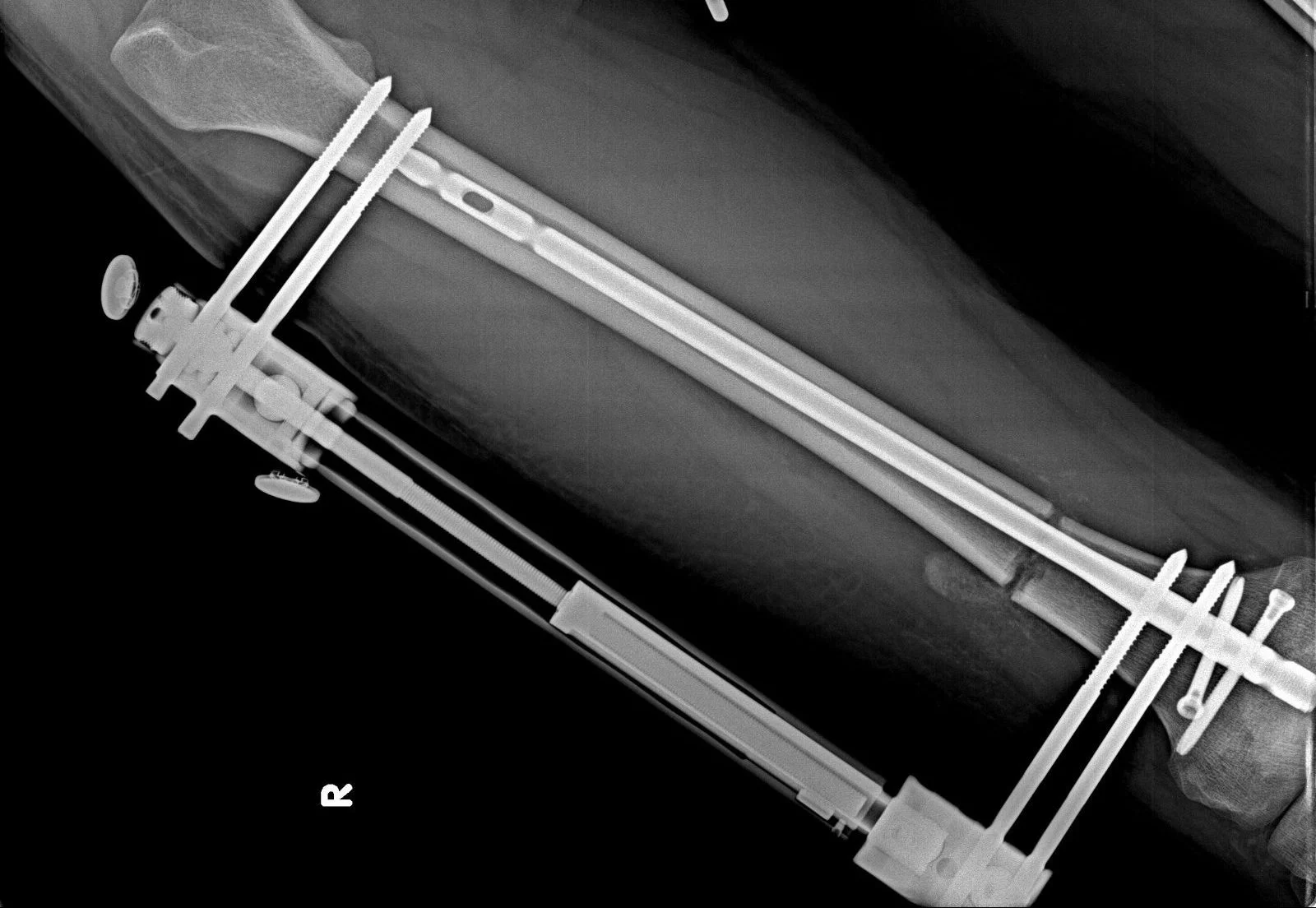
What are the types of Length Extension Surgery Treatments?
- What are the types of Length Extension Surgery Treatments?
- Lengthening osteotomy
- Guided Growth
- Ilizarov Method
- Monofocal Lengthening
- Bifocal Lengthening
Lengthening Osteotomy: This procedure involves cutting the bone and slowly lengthening it over time using an external fixator. The external fixator is a device that is attached to the bone using pins or screws. It is then used to slowly pull the bone apart, allowing new bone to grow in the gap. The process is typically done in small increments, usually 1mm per day, to allow the bone to heal properly. The procedure can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
Guided Growth: This procedure involves using a device to guide the growth of the bone. The device is typically a small, implantable rod that is inserted into the bone. It is then used to apply a small amount of force to the bone, which stimulates the growth plate and causes the bone to lengthen. The procedure is typically done in small increments, usually 1mm per day, to allow the bone to heal properly. The procedure can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
Ilizarov Method: This procedure involves using an external fixator to gradually lengthen the bone. The external fixator is a device that is attached to the bone using pins or screws. It is then used to slowly pull the bone apart, allowing new bone to grow in the gap. The process is typically done in small increments, usually 1mm per day, to allow the bone to heal properly. The procedure can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
Monofocal Lengthening: This procedure involves lengthening one bone at a time, usually the femur or tibia. This procedure is typically done in patients who have a significant difference in the length of their legs, and is typically done in conjunction with other procedures such as osteotomy or guided growth.
Bifocal Lengthening: This procedure involves lengthening two bones at the same time, such as the femur and tibia. This procedure is typically done in patients who have a significant difference in the length of their legs, and is typically done in conjunction with other procedures such as osteotomy or guided growth. This procedure can be more challenging than monofocal lengthening and requires a more experienced surgeon.
Lengthening osteotomy
Lengthening osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting the bone and slowly lengthening it over time using an external fixator. The procedure is typically used to correct leg length discrepancies, and can also be used to correct deformities or injuries to the bones.
The procedure begins with the surgeon making an incision over the bone that will be lengthened. The bone is then cut and an external fixator is attached to the bone using pins or screws. The external fixator is a device that is designed to slowly pull the bone apart, allowing new bone to grow in the gap. The process is typically done in small increments, usually 1mm per day, to allow the bone to heal properly.
The patient will typically be required to wear the external fixator for several months, depending on the amount of lengthening needed. During this time, physical therapy and exercises will be prescribed to help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
After the bone has been fully lengthened, the external fixator will be removed and the incision will be closed. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes several months to regain full strength and mobility.
It's important to note that there are potential risks and complications with this procedure, such as infection, nerve and blood vessel damage, and non-union of the bone. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.
Guided Growth
Guided growth is a surgical procedure that involves using a device to guide the growth of the bone. The device is typically a small, implantable rod that is inserted into the bone. It is then used to apply a small amount of force to the bone, which stimulates the growth plate and causes the bone to lengthen. The procedure is typically used to correct leg length discrepancies, and can also be used to correct deformities or injuries to the bones.
The procedure begins with the surgeon making an incision over the bone that will be lengthened.
The bone is then prepared and the implantable rod is inserted into the bone. The rod is then connected to a small external device that is worn by the patient. This device is used to apply a small amount of force to the bone, which stimulates the growth plate and causes the bone to lengthen. The process is typically done in small increments, usually 1mm per day, to allow the bone to heal properly.
The patient will typically be required to wear the external device for several months, depending on the amount of lengthening needed. During this time, physical therapy and exercises will be prescribed to help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
After the bone has been fully lengthened, the implantable rod and external device will be removed and the incision will be closed. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes several months to regain full strength and mobility.
It's important to note that there are potential risks and complications with this procedure, such as infection, nerve and blood vessel damage, and non-union of the bone. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.
Ilizarov Method
The Ilizarov Method, also known as the Ilizarov technique, is a surgical procedure that involves using an external fixator to gradually lengthen the bone. The external fixator is a device that is attached to the bone using pins or screws. It is then used to slowly pull the bone apart, allowing new bone to grow in the gap. The procedure is typically used to correct leg length discrepancies, and can also be used to correct deformities or injuries to the bones, such as fractures that did not heal properly.
The procedure begins with the surgeon making an incision over the bone that will be lengthened. The bone is then cut and the external fixator is attached to the bone using pins or screws. The external fixator is then used to slowly pull the bone apart, usually 1mm per day, to allow new bone to grow in the gap. This process can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
During this time, the patient will typically be required to wear the external fixator and will need to undergo regular physical therapy and exercises to maintain muscle strength and flexibility. The patient will also need to visit the surgeon regularly for adjustments and check-ups.
After the bone has been fully lengthened, the external fixator will be removed and the incision will be closed. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes several months to regain full strength and mobility.
The Ilizarov Method is considered a relatively safe and effective procedure, but as with any surgery, it carries some risks such as infection, nerve and blood vessel damage, and non-union of the bone. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.
Monofocal Lengthening
Monofocal lengthening is a surgical procedure that involves lengthening a single bone in the body. Unlike other types of lengthening procedures, such as the Ilizarov method which involves the use of an external fixator to gradually lengthen the bone, Monofocal lengthening typically uses an internal device that is implanted inside the bone. This device is used to slowly stretch the bone, allowing new bone to grow in the gap.
The procedure begins with the surgeon making an incision over the bone that will be lengthened. The bone is then cut and an internal device, such as an intramedullary nail, is implanted inside the bone. The internal device is then used to slowly stretch the bone, usually by 1mm per day, to allow new bone to grow in the gap. This process can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
During this time, the patient will typically be required to wear a cast or brace and will need to undergo regular physical therapy and exercises to maintain muscle strength and flexibility. The patient will also need to visit the surgeon regularly for adjustments and check-ups.
After the bone has been fully lengthened, the internal device will be removed and the incision will be closed. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes several months to regain full strength and mobility.
It's important to note that Monofocal lengthening is a relatively new procedure and has not yet been widely adopted. Also, as with any surgery, it carries some risks such as infection, nerve and blood vessel damage, and non-union of the bone. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.
Bifocal Lengthening
Bifocal lengthening is a surgical procedure that involves lengthening two bones simultaneously. This type of procedure is typically used to correct leg length discrepancies.
The procedure begins with the surgeon making an incision over the bones that will be lengthened. The bones are then cut, and an internal device, such as an intramedullary nail, is implanted inside each of the bones. The internal devices are then used to slowly stretch the bones, usually by 1mm per day, to allow new bone to grow in the gaps. This process can take several months to complete, depending on the amount of lengthening needed.
During this time, the patient will typically be required to wear a cast or brace and will need to undergo regular physical therapy and exercises to maintain muscle strength and flexibility. The patient will also need to visit the surgeon regularly for adjustments and check-ups.
After the bones have been fully lengthened, the internal devices will be removed and the incision will be closed. Recovery time can vary depending on the individual case, but it typically takes several months to regain full strength and mobility.
It's important to note that Bifocal lengthening is a relatively new procedure and has not yet been widely adopted. Also, as with any surgery, it carries some risks such as infection, nerve and blood vessel damage, and non-union of the bone. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with a qualified surgeon before proceeding.