What is Hip Bursitis?
- What is Hip Bursitis?
- What are the symptoms of hip bursitis?
- What causes hip bursitis?
- Can hip bursitis be prevented?
- How is bursitis treated?
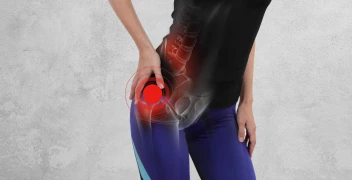
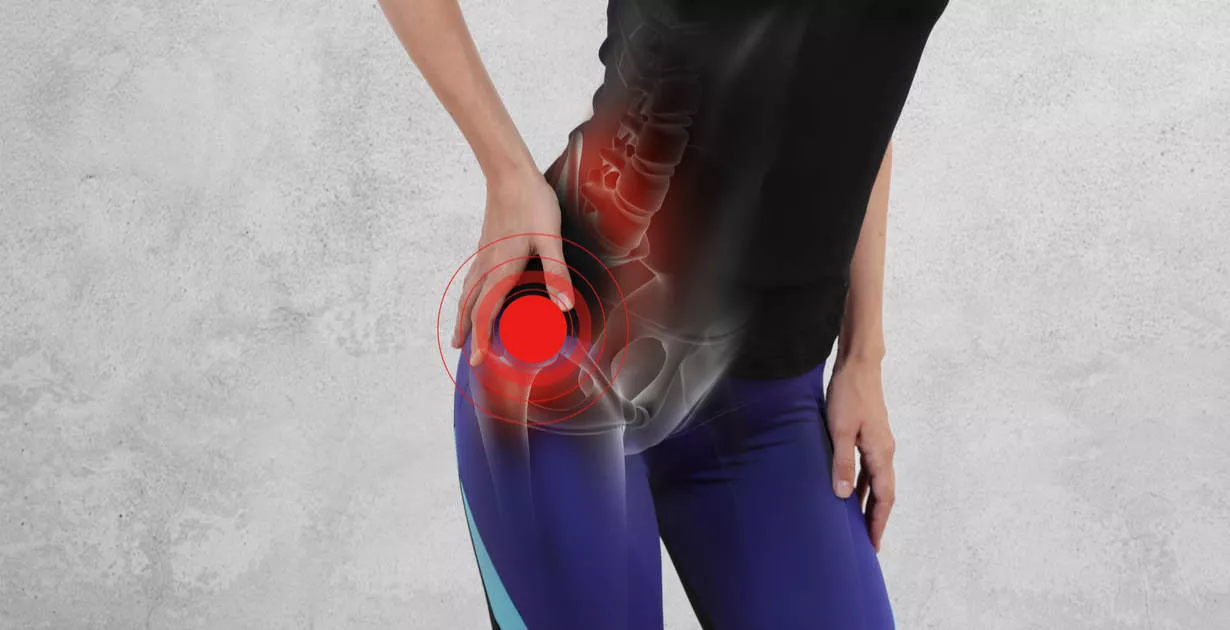
Bursitis is pain and swelling of the sac connecting the outer lateral bone and musculature of the hip. Tissue causing pain (bursa); They are fluid-filled sacs that hold your tendons, ligaments, muscles, and skin together. Normally, bursae help tendons, ligaments, and muscles move freely over the bone. But when the bursae swell, the tissues around them become very tender and painful. Trochanteric bursitis is swelling that affects the hip bursa.
Bursitis is not only found in the hip. It can also occur in the shoulder, knee and elbow. Bursitis can be acute (temporary) or chronic (permanent).
What are the symptoms of hip bursitis?
Symptoms are joint pain and tenderness. You may also have swollen in and around the affected area, and you may also feel warmth. The pain usually goes away in the first few days. Later, there may be pain as you move. You may feel it more when getting out of a chair or bed. You may also have pain when sitting for a long time and sleeping on the sore side.
Acute bursitis usually flares up quickly. Chronic bursitis goes away after a few days or weeks. Chronic bursitis pain may pass and the pain may recur. Acute bursitis can become chronic if the pain recurs or there is a hip injury.
Over time, the bursa can thicken, causing the swelling to worsen. This means that limited movement of the area can lead to weakening of the muscles.
What causes hip bursitis?
A few things can lead to hip bursitis, such as:
- Performing movements that force the hips excessively.
- Rheumatic joint inflammation.
- Bone spurs in the hip (bone growth above normal bone).
- Gout.
- Diabetes.
- Hip injury.
- Bacterial infection such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Spinal problems such as scoliosis.
- Irregular leg lengths.
How is hip bursitis diagnosed?
The doctor first performs a physical examination and then asks some questions. Sometimes he or she may order certain tests to be done to rule out other diseases that may cause similar symptoms. Like MRI and CT.
Can hip bursitis be prevented?
You can prevent bursitis by not making movements that will force your hips too much. Avoid particularly difficult and dangerous activities and take breaks during the day to rest your hips. Remember to warm up your muscles before you start exercising and then stretch them to prevent injury. If you are overweight, losing weight can help reduce pressure on the hips.
By strengthening your hips with a regular exercise routine, you can greatly reduce your risk of bursitis. Ask your doctor about the types of exercise that are right for you.
How is bursitis treated?
Bursitis treatment is usually provided by doing strengthening exercises and stretching movements. Thus, it helps to prevent muscle atrophy. You should avoid movements that cause pain. Ask your doctor about exercises that will help strengthen the sore area. Your bursitis can affect your social life. Therefore, you may need physical therapy to help you move around. It is often recommended for chronic bursitis.
You can use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen to reduce pain and swelling. You can also put an ice pack on the area to reduce swelling.
If these treatments don't work, you may need to have fluids removed from the bursa, or you may need steroid injections to reduce pain and swelling. Steroid injections are very effective in the treatment of bursitis. You may need a needle again after a few months.
Surgery is rarely required to treat bursitis. It is generally preferred when all treatments have failed. For people who need surgery, surgery is a simple procedure. The doctor removes the bursa from the hip and without the bursa, the hip can move normally. Surgery usually does not require a long hospital stay. Recovery time is usually short.
Living with hip bursitis
If you have chronic bursitis, gradually increase your movements and try to minimize flare-ups by stretching that area every day. And avoid activities that cause pain. Repeated physical activities are especially bad for bursitis. If you have a flare-up, remember that resting your hip is very important. Without proper rest, recovery is delayed.
Some questions to ask your doctor:
What causes my symptoms?
What is the best treatment option for me?
How soon will my symptoms go away?
Is it possible for my symptoms to recur?
Is it okay for me to exercise? What kind of exercises should I do?