Fibromyalgia: Definition, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
- Fibromyalgia: Definition, Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
- What Are the Symptoms of Fibromyalgia?
- What Are the Factors Leading to Fibromyalgia?
- How Is Fibromyalgia Diagnosed?
- Treatment Methods for Fibromyalgia
- Conclusion:
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by symptoms such as widespread muscle pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and sensitivity. It is often abbreviated as "FM" and fundamentally affects the functioning of the musculoskeletal system. Fibromyalgia is still not fully understood in the medical world, and its exact causes remain unidentified. Nevertheless, various approaches have been developed for managing and treating its symptoms.
What Are the Symptoms of Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is generally a chronic health condition that presents itself with widespread pain, fatigue, and various other symptoms. Symptoms can vary from person to person and their intensity can increase or decrease over time. Here are the most common symptoms of fibromyalgia:
- Widespread Pain: Individuals with fibromyalgia experience widespread and continuous pains. Pain is typically felt in various body regions, especially the neck, shoulders, back, hips, and knees. These pains generally emerge in deep areas of muscles and joints.
- Sensitivity: Fibromyalgia patients experience sensitivity at specific points. These points are referred to as "trigger points," and even slight touch on these areas can cause excessive pain.
- Fatigue: Fibromyalgia patients constantly feel fatigue and lack of energy. This feeling of fatigue doesn't subside despite rest and can negatively impact daily activities.
- Sleep Disorders: Individuals with fibromyalgia often struggle to obtain quality sleep. Problems such as difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, interruptions during sleep, and not feeling refreshed in the morning are commonly observed.
- Cognitive Issues: Fibromyalgia patients might experience problems like lack of concentration, mental fog, memory issues, and decreased mental sharpness. These symptoms are also referred to as "fibro fog."
- Migraines or Headaches: Migraine-like headaches are frequent among fibromyalgia patients. These headaches can be severe and adversely affect the quality of life.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Digestive system problems like irritable bowel syndrome are more commonly observed in fibromyalgia patients.
- Depression and Anxiety: A portion of fibromyalgia patients may also struggle with mental issues like depression and anxiety.
- Swelling and Tingling in Hands and Feet: Some patients might experience symptoms like swelling, tingling, or numbness in their hands and feet.
The symptoms of fibromyalgia can be complex and varied. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms, medical history, and physical examination.
What Are the Factors Leading to Fibromyalgia?
Although the exact causes of fibromyalgia are not fully understood, various factors are thought to contribute to the development of this chronic pain syndrome. Here are some factors believed to be associated with fibromyalgia:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history can increase the risk of fibromyalgia. Genetic factors are believed to influence an individual's susceptibility to this condition. However, along with genetic factors, environmental influences may also play a role in its onset.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalances: Neurotransmitters in the brain regulate functions such as pain perception, mood, and sleep patterns. Imbalances of neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine have been linked to fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Central Nervous System Sensitivity: The central nervous system of fibromyalgia patients might be more sensitive to pain and other stimuli. This can lead to an exaggerated response to stimuli that the body would normally tolerate.
- Infections: Certain viral or bacterial infections might trigger or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms. These infections could affect immune system responses, contributing to fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Trauma and Stress: Physical traumas (e.g., accidents or injuries) and prolonged psychological stress might play a role in the development of fibromyalgia. Chronic stress can increase inflammation in the body and lower pain thresholds.
- Sleep Disorders: Low sleep quality or sleep disorders like sleep apnea can worsen or trigger fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can intensify fibromyalgia symptoms. Hormones can influence pain thresholds and levels of inflammation in the body.
- Immune System Issues: Irregularities in the immune system can contribute to increased inflammation and the emergence of fibromyalgia symptoms.
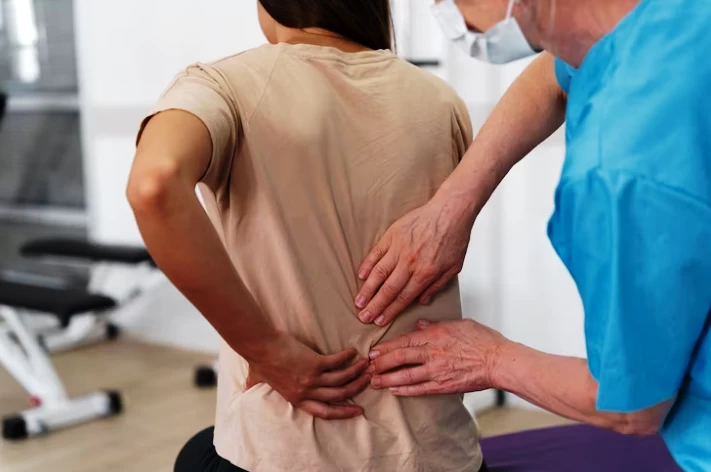
How Is Fibromyalgia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing fibromyalgia generally relies on symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. There isn't a specific laboratory test or imaging technique that can definitively diagnose fibromyalgia. The diagnosis process may include the following steps:
- Evaluation of Symptoms: The doctor assesses the patient's symptoms in detail. Information about widespread pain, fatigue, sleep disturbances, tender points, mental fog, and other symptoms is gathered.
- Review of Medical History: The patient's medical history, including past illnesses, injuries, surgeries, and family history, is taken into account. A family history of fibromyalgia could also be significant in the diagnosis process.
- Physical Examination: The doctor conducts a physical examination of the patient. They check pressure points, specifically tender points that are sensitive in fibromyalgia patients. Having tenderness in at least 11 of these points is considered one of the diagnostic criteria.
- Laboratory Tests: There isn't a specific laboratory test to diagnose fibromyalgia. However, the doctor might order certain laboratory tests to rule out other illnesses. These tests could include complete blood count, inflammation markers, and thyroid function tests.
- Differential Diagnosis: Before diagnosing fibromyalgia, other conditions with similar symptoms might need to be ruled out. Therefore, excluding other diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome is important.
- Criteria Matching: Generally, matching the criteria, such as experiencing widespread pain and other symptoms for at least 3 months, having sensitivity in tender points, is crucial for diagnosing fibromyalgia.
- Specialist Opinion: Specialists like physical medicine and rehabilitation doctors, rheumatologists, or pain specialists might also be involved in the diagnostic process.
It's important to note that diagnosing fibromyalgia can sometimes be intricate. Symptoms can overlap with other health issues, and the process might take time. Clearly expressing symptoms and health status to doctors can aid in an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Methods for Fibromyalgia
The goal of fibromyalgia treatment is to reduce symptom severity, enhance quality of life, and improve daily functionality. Treatment approach is generally personalized, as each patient's symptoms can differ, and various factors might be at play. Here are some methods used in fibromyalgia treatment:
- Medication: Various medications can be used to manage pain, improve sleep quality, and alleviate other symptoms. These medications might include pain relievers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and muscle relaxants.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy aims to strengthen muscles, increase flexibility, and enhance body mechanics. Techniques like exercises, manual therapy, and massage can be employed under the guidance of a skilled physical therapist.
- Exercise Programs: Regular and low-intensity aerobic exercises can assist in alleviating fibromyalgia symptoms. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can improve overall body conditioning.
- Stress Management and Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or supportive therapy can aid patients in coping with stress and improving mental health. Techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, and deep breathing might be incorporated.
- Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms. This includes balanced nutrition, regular sleep patterns, stress avoidance, and engaging in regular exercise.
- Alternative Treatment Approaches: Alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic treatment, yoga, and tai chi could alleviate symptoms in some fibromyalgia patients.
- Non-Pharmacological Treatments: Heat therapy, cold compresses, hydrotherapy, massage, and other physical methods can assist in coping with pain and discomfort.
The treatment approach is shaped by the patient's symptoms, lifestyle, overall health, and other factors. What's important is to collaborate with the doctor to create the best treatment plan and consistently review and adjust the treatment, as fibromyalgia treatment usually requires a personalized approach.
Conclusion:
Fibromyalgia is a complex syndrome characterized by symptoms like widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. Although its exact causes are not fully understood, various treatment methods exist to help patients manage their symptoms. Adopting a multidisciplinary approach aims to improve patients' quality of life and alleviate symptoms. While research on fibromyalgia continues, it's important for patients to collaborate with their doctors to create the most suitable treatment plan.