Stabilization Exercises for Posture: A Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Perspective
- Stabilization Exercises for Posture: A Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Perspective
- The Importance of Stabilization Exercises
- The Relationship Between Posture and Muscle Imbalance
- Main Goals of Stabilization Exercises
- How Stabilization Exercises Are Performed
- How Often Should Stabilization Exercises Be Done?
- Conclusion
Posture is an essential factor that determines the body’s alignment, movement, and function in daily life. Good posture helps maintain the balance of the musculoskeletal system, ensuring that all muscle groups are used equally, which prevents pain and injuries. Especially individuals who work long hours in office environments often face postural disorders due to incorrect sitting positions, immobility, and lack of support. To prevent and correct these issues, stabilization exercises play a significant role.
The Importance of Stabilization Exercises
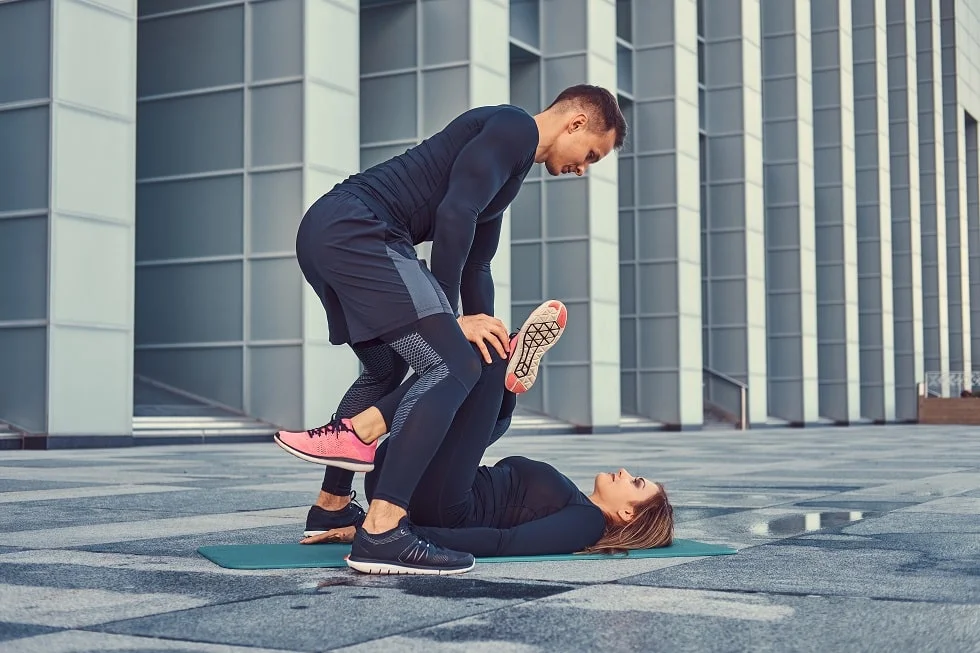
Stabilization refers to the effectiveness of the muscle groups required to maintain balance and control during movement. These exercises generally target the core, back, pelvic, and hip muscles, which are the central region of the body. These muscles connect the upper and lower parts of the body, protecting the spine and other joints.
Stabilization exercises play a crucial role in the treatment of many musculoskeletal conditions, such as back pain, herniated discs, shoulder, and neck problems. They also play a key role in improving posture. Stabilization exercises strengthen the muscles necessary for maintaining good posture, increase flexibility, and correct muscle imbalances.
The Relationship Between Posture and Muscle Imbalance
Posture requires muscles to work in harmony with each other. The weakening or overloading of a muscle group can lead to postural disorders in the body. For example, weak abdominal muscles may cause excessive load on the lower back, leading to back pain. Likewise, weak back muscles can lead to shoulder and neck pain.
Many people unknowingly live with poor posture. Long-term poor posture can create muscle imbalances, resulting in pain and discomfort. This is exactly where stabilization exercises come into play. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles needed for posture, correct muscle imbalances, and prevent pain.
Main Goals of Stabilization Exercises
Stabilization exercises serve several main purposes:
- Increase Muscle Strength: Strengthen stabilizer muscles, such as those in the abdomen, back, pelvis, and hips.
- Improve Posture: Ensure the proper alignment of the body, reduce pressure on the spine and joints.
- Enhance Flexibility: Increase muscle flexibility and improve the body’s range of motion.
- Correct Posture: Eliminate bad postural habits and promote correct posture.
- Reduce Pain: Alleviate musculoskeletal pain, especially in the lower back, neck, and shoulders.
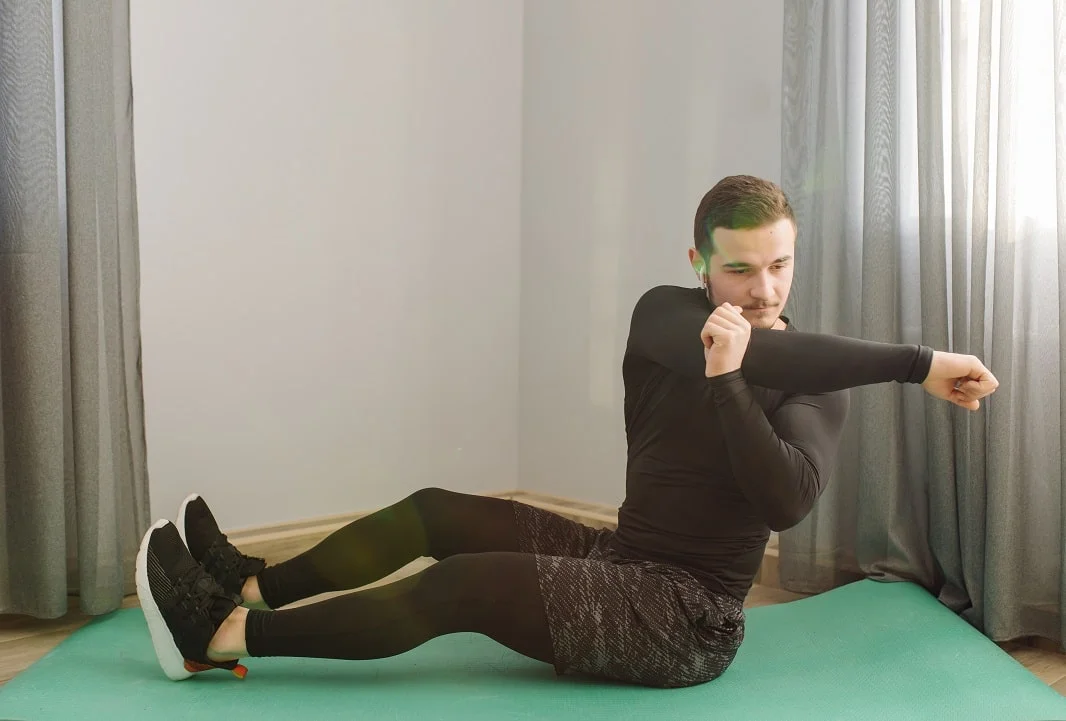

How Stabilization Exercises Are Performed
Stabilization exercises range from simple bodyweight movements to more complex exercises using specialized equipment. Below are some of the most common stabilization exercises:
1. Plank: The plank is an effective exercise for strengthening the abdominal, back, shoulder, and hip muscles. This exercise improves spinal stability and corrects posture. To perform the plank, position yourself on your hands and feet, keeping your body straight. Hold this position for a certain period, and gradually increase the duration over time.
2. Bridge: The bridge exercise primarily strengthens the pelvic region muscles. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Then, lift your hips towards the ceiling, forming a straight line from your shoulders to your knees. This exercise helps relieve lower back pain and improves posture.
3. Dead Bug: The dead bug exercise targets the abdominal and back muscles. Lie on your back with your hands behind your head and your knees bent. Extend one leg straight out while keeping your other leg and arm in place. Alternate the movements, ensuring that your core remains engaged throughout the exercise. This exercise improves the function of abdominal muscles and enhances spinal stability.
4. Bird Dog: The bird dog is another exercise that strengthens the abdominal and back muscles. Start on your hands and knees. Simultaneously extend one arm and the opposite leg while maintaining stability in your core. Focus on controlling your spine throughout the movement.
5. Leg Raises: Lie on your back and raise one leg straight up while holding it for a few seconds before lowering it. This exercise strengthens the lower abdominal muscles and improves lower back stability.
How Often Should Stabilization Exercises Be Done?
The effectiveness of stabilization exercises depends on regular practice. Initially, it is recommended to perform these exercises 3-4 times a week. Each exercise can be performed for 10-15 repetitions, and over time, the number of sets and repetitions can be increased. However, as each individual’s physical condition differs, exercise programs should be customized and supervised by a physiotherapist.
Conclusion
Stabilization exercises play a vital role in improving posture and maintaining the stability of the musculoskeletal system. They not only alleviate pain but also enhance muscle strength and overall body function. However, performing these exercises with proper technique is crucial to minimizing the risk of injury and achieving the best results.
If you are experiencing postural issues or wish to begin an exercise program, seek support from a physiotherapist to develop a personalized plan. Remember, every individual’s needs are different, so the right approach is always the most important factor.

Dr. Elif Berber