What is Gout?
- What is Gout?
- What are the symptoms of gout?
- How is gout diagnosed?
- How is gout treated?
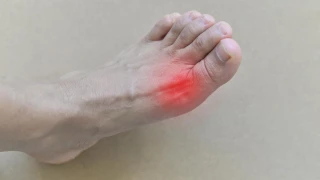
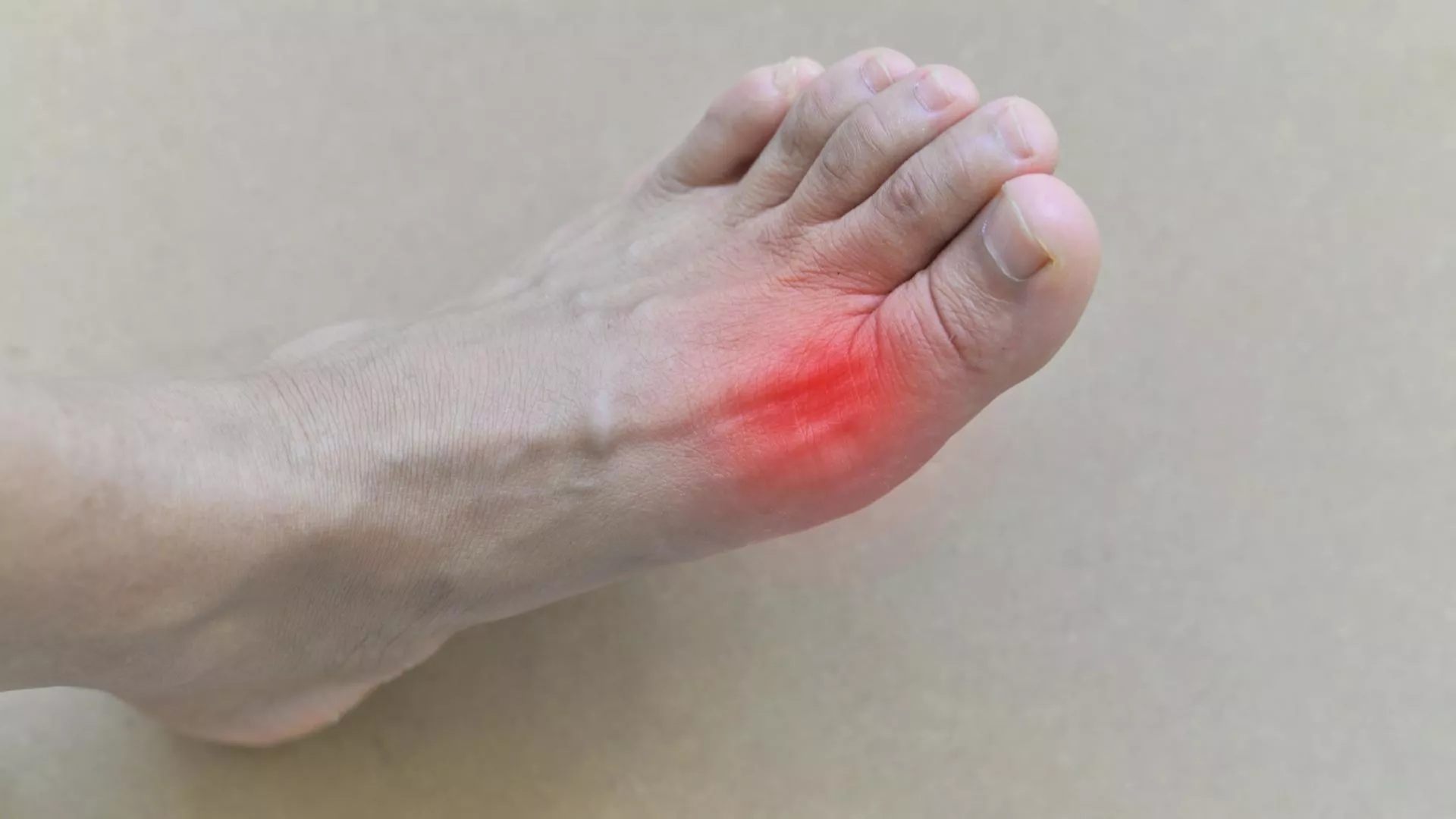
- Gout is a painful and difficult condition in which the uric acid level is high. Not everyone with high levels of uric acid in the blood (called hyperuricemia) will develop gout. It is not known exactly why gout develops in patients with hyperuricemia.
- Although the joints are the most affected part of the body, other parts of the body are also affected. Uric acid can build up in the kidney or urinary tract and kidney stones may form or kidney function may be impaired. Kidney stones caused by uric acid crystals occur in about 15 percent of people with gout.
- Gout is more common in men aged 30-45 and women aged 55-70.
The following conditions increase the risk of developing gout:
- Hypertension
- Being operated
- Obesity
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Overeating
- Excessive meat and fish consumption
- Taking medications (especially diuretics) that affect uric acid levels
What are the symptoms of gout?
Gout is manifested by attacks. During these attacks, redness, swelling, sudden severe joint pain and tenderness occur in the joints. Although a seizure usually only affects one joint, it can develop in more than one joint at the same time. The pain and swelling may get worse within a few hours.
How is gout diagnosed?
There are diseases that can cause joint pain and inflammation. While a person with gout has no symptoms for a while, severe joint pain in acute attacks suggests gout.
To diagnose gout, the acid level is checked. Additionally, fluid may be drawn from the affected joint to look for uric acid crystals.
Gout can also be diagnosed from a person's symptoms and physical exam.
How is gout treated?
Anti-inflammatory drugs treat acute gout attacks best.
For people with a history of gout, treatment is an important factor in reducing the pain and severity of another attack.
The gout diet is important for reducing seizures and balancing uric acid in the body.
Diet can reduce the frequency of gout attacks. Since obesity is a risk factor, losing weight is also important to prevent many other health problems (heart disease, diabetes, hypertension).
Foods that should be consumed less in the diet of gout patients:
- Red meat
- Sea products
- Beer and spirits (e.g., gin, vodka)
- High fructose foods and drinks
Recommended food and drinks:
- Coffee
- Foods based on complex carbohydrates (whole grains, brown rice, oatmeal, beans)
- Low-fat milk, dairy products
- Vitamin C