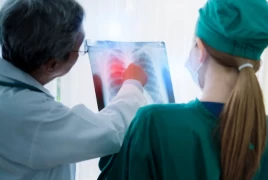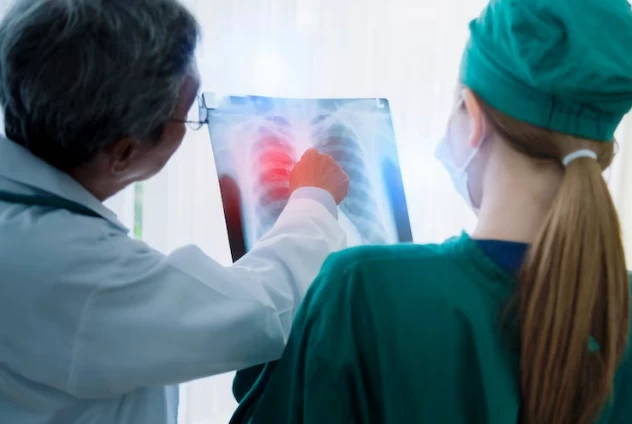
Lung Cancer and Thoracic Surgery: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Advances
- Lung Cancer and Thoracic Surgery: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Advances
- What Are the Factors Leading to Lung Cancer?
- Definition and Classification of Lung Cancer
- Diagnostic Methods for Lung Cancer
- Treatment Options in Thoracic Surgery for Lung Cancer
- Surgical Outcomes and Advances
- In Conclusion,
Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide and is particularly associated with environmental factors such as smoking habits. Thoracic surgery encompasses the treatment and surgical interventions for patients diagnosed with lung cancer. In this article, we will discuss the key features of lung cancer, diagnostic methods, treatment options related to thoracic surgery, and the outcomes of surgical interventions.
What Are the Factors Leading to Lung Cancer?
The factors contributing to lung cancer can involve a complex combination. The most significant risk factors are listed below:
- Smoking: The most common and potent risk factor. Smoking accounts for over 85% of lung cancer cases. Chemicals in cigarettes can harm lung tissues and promote the formation of cancer cells.
- Passive Smoking: Non-smokers exposed to secondhand smoke are also at risk. Exposure to cigarette smoke at home or in the workplace can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Radon Gas: Radon is a naturally occurring gas found in soil and can accumulate in enclosed spaces. High radon levels can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Occupational Exposure: Exposure to chemicals like asbestos, arsenic, nickel, chromium, and benzene or industrial dust can elevate the risk of lung cancer.
- Air Pollution: Prolonged exposure to air pollution, especially in individuals breathing polluted air, can raise the risk of lung cancer.
- Family History: Those with a family history of lung cancer may be at an increased risk. This can stem from both genetic factors and shared environmental exposures.
- Radiation Exposure: High-dose radiation exposure to the chest area (e.g., radiation therapy for cancer treatment) can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Other Chronic Lung Diseases: Other lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can heighten the risk of lung cancer.
- Dietary Factors: Unhealthy eating habits, inadequate consumption of fruits and vegetables, can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic factors can influence an individual's risk of lung cancer. However, environmental factors often outweigh genetic predisposition.
An important point to remember is that multiple risk factors can interact. For instance, a person who smokes and is also exposed to radon can have an even higher risk. The most crucial step to reduce the risk of lung cancer is to avoid smoking or quit smoking.
Definition and Classification of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the result of uncontrolled and abnormal growth of cellular structures within the lungs, resulting in a tumor. There are two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is more common and can be further categorized into subtypes like adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma, while SCLC is more aggressive.
Diagnostic Methods for Lung Cancer
The diagnosis of lung cancer usually involves imaging methods and examination of tissue samples. Techniques like computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) help assess the tumor's size, spread, and other characteristics. To confirm the diagnosis, procedures such as bronchoscopy or biopsy are conducted to examine cancer cells under a microscope.
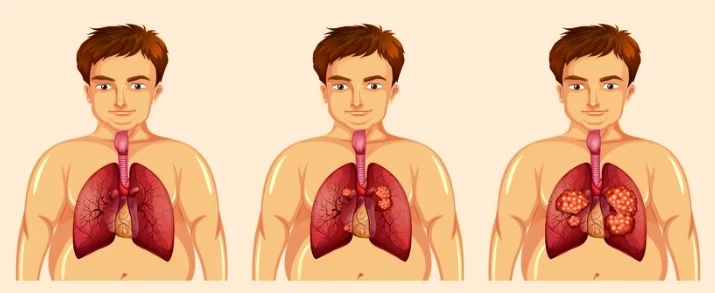
Treatment Options in Thoracic Surgery for Lung Cancer
Thoracic surgery can be an effective treatment option for patients with early-stage NSCLC or in certain cases of SCLC. The treatment approach is determined by factors such as tumor type, stage, and the patient's overall health. Surgical options may include:
- Lobectomy: The most commonly performed method, involving the removal of a lung lobe.
- Pneumonectomy: The complete removal of an entire lung.
- Segmentectomy: Removal of only the section of the lung where the tumor is located.
- Wedge Resection: Removal of a portion of healthy tissue surrounding the tumor.
Surgical Outcomes and Advances
The success of thoracic surgery in lung cancer treatment depends on the tumor's stage, the patient's general health, and surgical expertise. Surgery can lead to complete recovery in early-stage NSCLC patients. However, surgery alone might be insufficient in advanced-stage diseases, requiring additional treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapies.
In recent years, advancements in surgical techniques and technologies have made minimally invasive surgical methods more common. Approaches like robotic surgery and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery allow faster patient recovery and reduced complications, while enhancing the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
In Conclusion,
Lung cancer is a serious health issue that can be treated with early diagnosis and appropriate interventions. Thoracic surgery plays a significant role in lung cancer treatment and has the potential to improve patients' quality of life. However, since each patient is unique, individualized treatment approaches and a multidisciplinary approach are crucial.