Silent Night, Audible Danger: The Unknown Face of Snoring
- Silent Night, Audible Danger: The Unknown Face of Snoring
- What Is Snoring?
- What Are the Causes of Snoring?
- What Problems Does Snoring Cause?
- What Are the Treatment Options for Snoring?
- What Steps Can Be Taken to Prevent Snoring?
What Is Snoring?
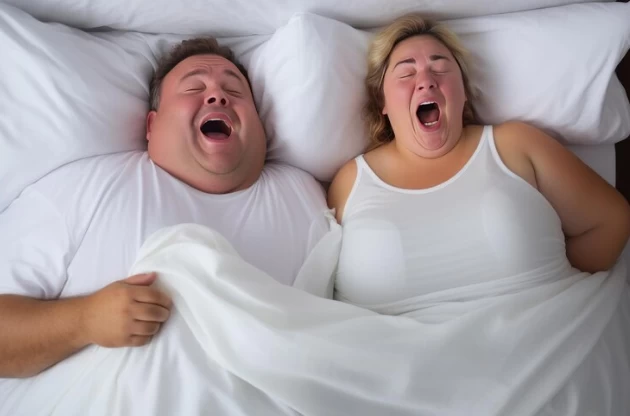
Snoring is a common problem for many people and often negatively affects the quality of sleep. Snoring refers to the sound produced by the vibrations in the airway during the night, and this condition can disrupt the sleep of the person who is asleep and their partner or others in the same room. In this article, we will explore the causes of snoring, treatment options, and steps to prevent snoring.
What Are the Causes of Snoring?
- Throat and Palate Issues: Among the most common causes of snoring are the relaxation of throat and palate tissues. The relaxation of these tissues can lead to narrowing of the airway and snoring.
- Nasal Congestion: Nasal congestion can lead to airflow through the mouth instead of the nose, triggering snoring. Factors such as allergies, colds, and nasal polyps can cause nasal congestion.
- Obesity: Excess weight can cause the accumulation of extra fat around the neck, narrowing the airway and promoting snoring.
- Alcohol and Sleep Medications: Alcohol consumption and certain sleep medications can lead to a decrease in muscle tone and an increase in snoring.
- Sleep Position: Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and palate tissues to obstruct the airway, increasing snoring.
- Aging: Aging can lead to the relaxation of throat tissues and an increased risk of snoring.
- Genetic Factors: Family history can influence the tendency to snore. Genetic factors determine the structural characteristics of the airways, which can increase susceptibility to snoring.

What Problems Does Snoring Cause?
Although snoring may seem like a problem that only disturbs sleep, it can be a symptom that leads to serious health problems in the long run. Some potential problems caused by snoring include:
- Reduced Sleep Quality: Snoring can disrupt the sleep quality of both the snorer and those sleeping in the same room. Persistent snoring can make it difficult to transition into deep sleep, leading to feelings of unrest.
- Risk of Sleep Apnea: Among the underlying causes of snoring are signs of serious respiratory disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA causes recurrent airway obstructions during sleep, potentially leading to interruptions in breathing during sleep. This condition can lead to reduced oxygen levels, cardiovascular problems, and even an increased risk of stroke or heart attack.
- Daytime Sleepiness: Chronic snorers may experience problems such as insomnia and daytime sleepiness, affecting their daytime performance.
- Relationship Issues: Snoring can negatively affect the sleep of partners or those living in the same house, potentially leading to relationship tensions.
- Concentration and Focus Problems: Sleep deprivation and related issues can affect work or school performance, causing difficulties in concentration and focus.
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): Persistent snoring, when associated with sleep apnea, can contribute to hypertension. This can pose a serious threat to cardiovascular health.
- Tongue and PalateProblems: In some cases, snoring leads to persistent mouth breathing, resulting in dryness and irritation of the mouth and throat tissues.
- Sleep Apnea-Related Problems: If snoring is a sign of sleep apnea, it can lead to reduced oxygen levels, irregular heart rhythms, and an increased risk of stroke or heart attack.
What Are the Treatment Options for Snoring?
Various methods are available for treating snoring. It is important to consult an ear, nose, and throat specialist to determine the appropriate treatment method. Here are some snoring treatment options:
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes such as weight loss (if overweight), limiting alcohol and sedative use, and avoiding sleeping on your back can help reduce snoring.
- Snoring Mouthpieces: These devices can hold the upper and lower jaws together, preventing the airway from being obstructed.
- CPAP Devices: For individuals experiencing serious respiratory problems related to snoring, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices may be recommended. These devices keep the airway open during sleep.
- Surgical Interventions: When non-pharmacological treatments are ineffective, or when anatomical issues continue to cause snoring, surgical interventions may be considered. These interventions may include uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) and uvulopalatal flap (UPF) procedures.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Prevent Snoring?
To prevent or reduce snoring, consider the following steps:
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco can help reduce snoring.
- Change Sleep Position: Opt for sleeping on your side or stomach instead of your back to reduce snoring.
- Manage Allergies: Using allergy medications or air purifiers to control allergic reactions can reduce nasal congestion.
- Establish Regular Sleep Patterns: Maintaining consistent sleep schedules can improve sleep quality and reduce snoring.
In conclusion, snoring is a common problem for many people, but there are treatment options available. If snoring affects your sleep or that of your partner, consult with an ear, nose, and throat specialist. With appropriate treatment options and lifestyle changes, you can reduce snoring and achieve a better quality of sleep.