Obesity Surgery
- Obesity Surgery
- What is Obesity?
- Why Is Obesity Treatment Important?
- What is Obesity Surgery?
- What Are the Most Common Bariatric Surgery Procedures?
- When Should Obesity Surgery Be Considered?
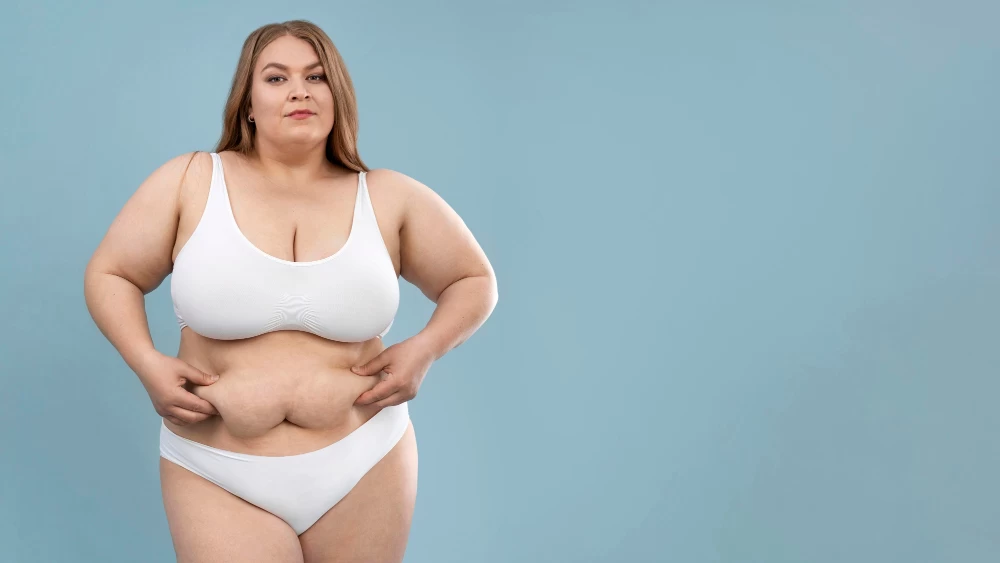
What is Obesity?
Let's start with the definition of obesity first. Obesity is a health condition characterized by excessive accumulation of fat in the body. Obesity is defined when a person's body mass index (BMI) is above a certain limit. BMI is calculated by taking into account a person's weight, height, and gender.
Obesity usually develops as a result of the disruption of the balance between energy intake and expenditure. Regular intake of large amounts of energy, especially the consumption of foods containing high fat and sugar, is one of the main causes of obesity. However, there are many factors that affect obesity. These:
- - Nutritional habits: Excessive consumption of low-nutrient, high-calorie foods increases the risk of obesity.
- - Lack of physical activity: Not exercising regularly or not being physically active contributes to obesity by reducing energy expenditure.
- - Genetic factors: Obesity may be associated with the presence of obese individuals in the family. Certain genetic factors can affect metabolic rate, fat storage and energy use.
- - Metabolic factors: Conditions such as thyroid gland problems, hormonal imbalances and some metabolic syndromes can lead to obesity.
- - Psychosocial factors: Psychological factors such as stress, depression, low self-esteem, emotional eating can increase the risk of obesity.
Why Is Obesity Treatment Important?
Obesity is a condition that causes a variety of health problems. It is closely related to a number of complications such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, joint problems, respiratory problems, some types of cancer and psychological problems.

What is Obesity Surgery?
Obesity surgery is a treatment method in which surgical interventions are applied to promote weight loss in overweight or obese individuals. Bariatric surgery is a preferred option to reduce obesity-related health problems and improve quality of life.
Bariatric surgery uses a variety of surgical procedures to accelerate the weight loss process, including reducing stomach volume, partially disabling the intestines, or altering the gastrointestinal connection. These procedures are determined by the individual's level of obesity, general health, and surgical risks.
What Are the Most Common Bariatric Surgery Procedures?
The most common bariatric surgery procedures are:
- Gastric Bypass: In this procedure, a small portion of the stomach is created, reducing the amount of nutrition and bypassing a portion of the intestines. In this way, both stomach volume is reduced and nutrient absorption is reduced.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this procedure, most of the stomach is removed and a smaller tube-shaped stomach is left behind. This both reduces stomach volume and reduces the feeling of hunger.
- Biliopancreatic Diversion: In this procedure, part of the stomach is removed and the intestines are redirected. Both stomach volume is reduced and nutrient absorption is greatly reduced.
Bariatric surgery can accelerate the weight loss process and improve obesity-related health problems. However, every surgical intervention involves some risks and post-surgical complications may occur. Therefore, if bariatric surgery is being considered, it is important to inform the individual in detail about the pre-surgical evaluation, risks, and benefits. In addition, bariatric surgery provides the opportunity not only to achieve weight loss, but also to maintain long-term weight control with lifestyle changes.
When Should Obesity Surgery Be Considered?
Bariatric surgery is generally considered in cases where weight loss goals cannot be achieved or in individuals with serious obesity-related health problems. However, bariatric surgery is often used only as a tool towards weight loss and is recommended to be combined with other measures such as lifestyle changes, regular exercise and healthy eating.