Who is at Risk for Colon Cancer?
- Who is at Risk for Colon Cancer?
- What is Colon Cancer?
- Factors Contributing to Colon Cancer
- Symptoms of Colon Cancer
What is Colon Cancer?
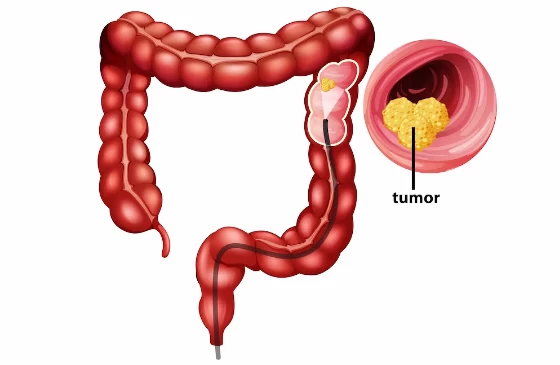
The colon is a part of the digestive system, extending from the small intestine, where the liquid portion of undigested food is absorbed and eliminated. Colon cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancerous) cells develop on the inner surface of the large intestine (colon). The last portion of the large intestine, located near the rectum, is called the rectum. Therefore, the terms "rectal cancer" and "colon cancer" will be used interchangeably in this article. Cancer occurs when normal cells proliferate uncontrollably and irregularly, forming tumors. Over time, these tumors can grow and spread to surrounding tissues. This process is called metastasis and can lead to the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Factors Contributing to Colon Cancer
Various factors can contribute to the development of colon cancer. While some factors might be associated with genetic predisposition, environmental and lifestyle factors also play a significant role. Key factors contributing to colon cancer include:
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history is one of the most significant factors influencing colon cancer risk. Individuals with a family history of colon cancer may be at risk, especially if there are multiple cases of colon or rectal cancer in the family.
- Age: The risk of colon cancer increases with age, becoming more pronounced after the age of 50.
- Dietary Habits: Consuming high amounts of red meat and processed meat (such as sausages and bacon) can increase the risk of colon cancer. Additionally, low-fiber, high-fat, and high-calorie diets can also be risk factors.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of regular physical activity can lead to obesity, which, in turn, increases the risk of colon cancer.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can raise the risk of colon cancer.
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, especially Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease, can elevate the risk of colon cancer.
- Polyps: Polyps present on the inner lining of the intestines that can transform into cancerous growths can increase the risk of colon cancer. Adenomatous polyps, in particular, are considered precursors to cancer.
- Hereditary Syndromes: Certain genetic syndromes can elevate the risk of colon cancer. Syndromes like Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer) carry a very high risk of colon cancer.
- Environmental Factors: Some environmental factors, particularly polluted water and food, are thought to increase the risk of colon cancer. However, research in this area is still ongoing.
Factors influencing colon cancer development can interact in complex ways. Taking steps to reduce risk factors, such as adopting healthy dietary habits, engaging in regular physical activity, and limiting smoking and alcohol consumption, is important.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer may not initially show symptoms or the symptoms might be very mild. However, as the tumor advances or grows larger, more distinct symptoms may emerge. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if any symptoms are noticed. Common symptoms of colon cancer include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramps: Colon cancer can lead to intestinal obstruction or pressure, causing abdominal pain and cramps.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Sudden and noticeable changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, may occur.
- Blood in Stool: Seeing bright red or dark-colored blood in the stool could be a sign of colon cancer. However, this symptom does not always indicate colon cancer; it can also point to other digestive issues.
- Anemia Due to Blood Loss: Cancerous tumors can damage blood vessels, leading to chronic blood loss and, subsequently, anemia (iron deficiency). Anemia can manifest as fatigue, weakness, and pale skin.
- Weight Loss: Rapid weight loss can occur due to the spread of cancer or nutritional issues as the colon cancer progresses.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Individuals with colon cancer often experience weakness and fatigue. This could be due to the effects of cancer on metabolism.
- Sensation of Bowel Movements: A feeling of bowel movement or a sensation of fullness during bowel evacuation may occur.
- Loss of Appetite: As colon cancer advances, loss of appetite and a general feeling of weakness may develop.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Tumors disrupting normal bowel function can lead to nausea and vomiting.
- Gas and Bloating: Colon cancer can lead to intestinal obstruction or constriction, resulting in gas and bloating.
It's important to note that these symptoms can be present in various other conditions or situations. Consulting a doctor and undergoing necessary tests if any symptoms arise is essential. Early diagnosis can increase the chances of catching colon cancer in its early stages, improving the likelihood of successful treatment and recovery.