My Opinions on Contraceptive Methods as an Obstetrician and Gynecologist
- My Opinions on Contraceptive Methods as an Obstetrician and Gynecologist
- Contraceptive Methods
- Which Method Is Right for Whom?
- In Conclusion
Throughout my career as an obstetrician and gynecologist, I have guided thousands of women in making decisions related to fertility. Every woman’s relationship with fertility is unique. While some place motherhood at the center of their lives, others may choose to focus on their careers. Some are content with having one child, while others plan to have three or four. Just as these decisions are deeply personal, the means of implementing them should be equally scientific and well-planned. This is where effective contraception methods—options for preventing pregnancy—come into play.
In this article, I would like to present the contraceptive methods I frequently encounter in my practice and recommend to my patients, along with their advantages and disadvantages. My aim is to help each individual choose the method that best suits their lifestyle, health status, and expectations.
Contraceptive Methods
1. Natural Methods::These are methods that rely on the body’s natural cycle without the use of medication or devices. These methods are generally recommended only when other methods are not feasible, as they are far behind modern medical standards.
- a. Calendar Method (Rhythm Method): Based on calculating the days of ovulation according to the menstrual cycle. Theoretically, the three days before and after ovulation are considered high-risk days.
- Advantages: Natural, cost-free, hormone-free.
- Disadvantages: Ineffective for women with irregular cycles; requires attention and regular tracking. Has a low protection rate.
- b. Withdrawal Method: Involves the male partner withdrawing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation.
- Advantages: Easy and cost-free.
- Disadvantages: Very low effectiveness; depends on the male partner’s self-control. There is a high failure rate due to the presence of sperm in the pre-ejaculate fluid.
2. Barrier Methods:
These physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
- a. Condom: While there are male and female versions, the male condom is the most commonly used.
- Advantages: Prevents both pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections.
- Disadvantages: Prone to user error; may tear or slip during intercourse. Must be used consistently with every act of intercourse.
- b. Diaphragm and Cervical Cap: Devices placed inside the vagina by the woman to cover the cervix.
- Advantages: Hormone-free, allows personal control.
- Disadvantages: Requires knowledge of correct placement and timing. Not widely used.
3. Hormonal Methods:
These work by suppressing ovulation or making the uterine environment hostile to sperm using hormone-based medications.
- a. Birth Control Pills: Taken daily and contain estrogen and progesterone.
- Advantages: Regulates menstruation, reduces acne, and provides protection against ovarian and uterine cancers.
- Disadvantages: Must be taken at the same time every day. Effectiveness decreases if doses are missed. May cause nausea or breast tenderness in some women.
- b. Mini Pill: Contains only progesterone and is particularly suitable for breastfeeding women.
- Advantages: Safe to use during breastfeeding.
- Disadvantages: May cause menstrual irregularities. Timing of intake is more critical.
- c. Monthly or Three-Month Injections: Long-acting injections administered intramuscularly.
- Advantages: Eliminates the risk of forgetting. The three-month version provides extended protection.
- Disadvantages: May cause menstrual irregularities, weight gain, and decreased bone density.
- d. Subdermal Implant (Rod): A small rod placed under the skin of the upper arm that releases low-dose progesterone over three years.
- Advantages: Long-term protection, eliminates user error.
- Disadvantages: May cause menstrual irregularities; placement requires a minor surgical procedure.
4. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs):
T-shaped devices placed inside the uterus. Available in non-hormonal (copper) and hormonal (levonorgestrel) types.
- a. Copper IUD: Prevents fertilization by impairing sperm mobility.
- Advantages: Hormone-free, effective for up to 10 years.
- Disadvantages: May increase menstrual bleeding.
- b. Hormonal IUD: Releases a low dose of progesterone. Reduces or may even stop menstrual bleeding.
- Advantages: Ideal for women with heavy and painful periods; effective for up to 5 years.
- Disadvantages: May cause pain during insertion; spotting may occur during the initial months.
5. Permanent Methods (Sterilization):
These are surgical procedures used to permanently prevent fertility in individuals who no longer wish to have children.
- a. Tubal Ligation (in Women): Involves cutting or tying the fallopian tubes.
- Advantages: Highly effective and permanent.
- Disadvantages: Involves surgery; reversal is not guaranteed.
- b. Vasectomy (in Men): Involves cutting or sealing the sperm ducts.
- Advantages: Highly effective and a simple procedure for men.
- Disadvantages: Reversal is unlikely.
6. Emergency Contraception (Morning-After Pill):
Hormonal pills taken within 72 hours after unprotected sex.
- Advantages: Significantly reduces the risk of pregnancy.
- Disadvantages: Not suitable for frequent use. May cause menstrual irregularities.
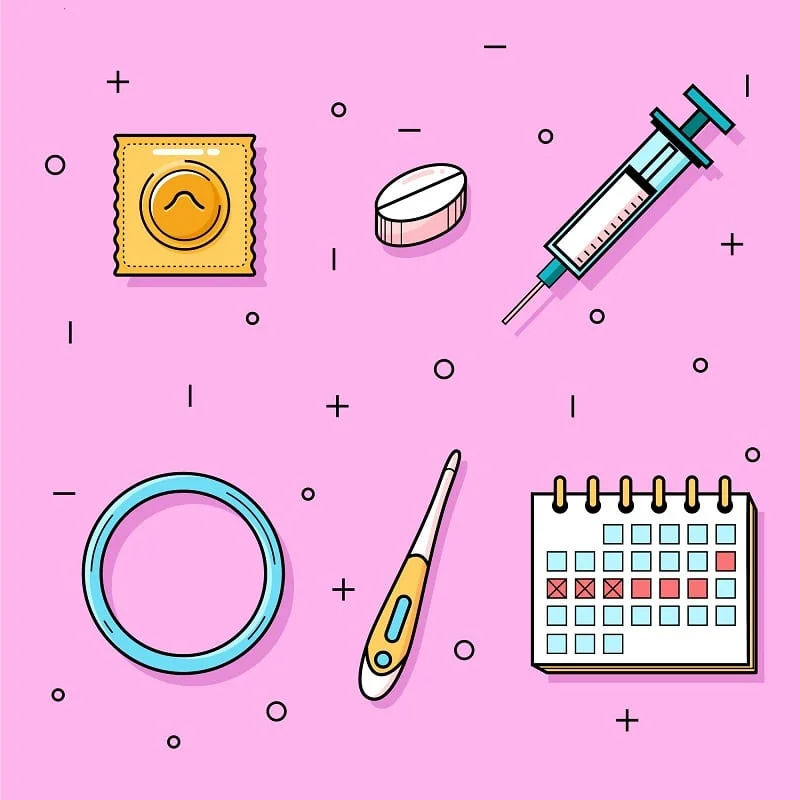
Which Method Is Right for Whom?
As I always tell my patients, contraception must be tailored to the individual. Age, overall health, fertility plans, partner dynamics, level of sexual activity, and personal preferences all play a role in determining the right method.
The recommendation I give to a young university student may differ greatly from the one I provide to a woman who is already a mother of three. That’s why, in my clinic, I prioritize patient privacy and open communication to help each woman determine the most appropriate contraceptive method for her life.
Our goal is not just to prevent unwanted pregnancies but also to support a woman’s hormonal balance, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
In Conclusion
Contraceptive methods are among the most empowering tools for modern women to plan their lives. With accurate information, correct usage, and regular medical follow-ups, a healthy sexual life is entirely achievable.
Remember, every decision regarding your body is your right; my role is to guide you scientifically on that journey.
With love and health,

Op. Dr. Kadir Şahin
Obstetrician and Gynecologist